LCD TV structure and operating principle
Judging by the number of models sold, LCD TVs have firmly taken a leading position in the market and in the hearts of TV viewers. Today, this type is chosen for its optimal price/quality ratio with minimal power consumption. In this article we will talk about LCD TVs, reveal the secret and principle of their operation, pros and cons.
REFERENCE. The name of these LCD devices comes from the English Liquid Crystal Display, which literally translates as liquid crystal screen. LCD and LCD are names of the same type of TV.

The content of the article
Device: how an LCD TV works
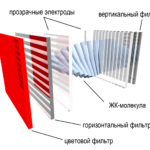
An LCD or LCD system, as the name suggests, consists of an array of similar elements - a system of liquid crystals, color filters - with the help of which an image is formed, protective glass, and a source of changing light.
 The crystal system is uniformly illuminated from the outside by a cold cathode fluorescent lamp. The operation of the panel itself depends on its location - the passage or reflection of the beam will occur. When there is no external influence, light passes freely through polarizers. The backing is visible. Liquid crystals (pixels) are controlled by applying a potential difference (voltage) to them. The magnitude of this voltage determines how much the crystal will rotate, and therefore the polarization angle. Its brightness depends on the degree of polarization.Accordingly, the crystal transmits more light, and the dot on the screen is brighter. Then the light beam passes through a polarizing filter perpendicular to the flow, a color filter and passes onto the screen.
The crystal system is uniformly illuminated from the outside by a cold cathode fluorescent lamp. The operation of the panel itself depends on its location - the passage or reflection of the beam will occur. When there is no external influence, light passes freely through polarizers. The backing is visible. Liquid crystals (pixels) are controlled by applying a potential difference (voltage) to them. The magnitude of this voltage determines how much the crystal will rotate, and therefore the polarization angle. Its brightness depends on the degree of polarization.Accordingly, the crystal transmits more light, and the dot on the screen is brighter. Then the light beam passes through a polarizing filter perpendicular to the flow, a color filter and passes onto the screen.
IMPORTANT. Pixels on a TV screen never go out; they can only change their polarization, i.e. the intensity of the glow. Therefore, the image does not disappear, but gradually changes frame by frame.
To summarize, it works like this: the light flux is filtered by a matrix consisting of many individual pixels that form a network. Three primary colors pass through this filter - blue, red and green, and when they are combined with each other, a color picture is formed on the screen.
Notes
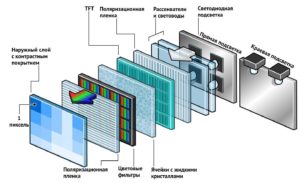
 Modern technologies allow you to apply voltage to any crystal of each of the layers of the matrix. Each layer of the matrix is important, but the main role is given to the first two, which are made of pure, sodium-free glass, called the substrate. It is between them that the liquid crystals are located, or, to be precise, their thinnest layer.
Modern technologies allow you to apply voltage to any crystal of each of the layers of the matrix. Each layer of the matrix is important, but the main role is given to the first two, which are made of pure, sodium-free glass, called the substrate. It is between them that the liquid crystals are located, or, to be precise, their thinnest layer.- Colored image - the result of using a matrix of passive filters, which, by dividing the white color source, produce three main ones - blue, red and green. Using their combination, any color palette can be obtained.
- If the polarization angle of the liquid crystal crystal becomes 90º relative to the passive filter, light does not pass through it.
- Time response The rate of rotation of the crystal is calculated when voltage is applied to it. It is reduced by increasing the potential difference, and the rotation occurs faster. The clarity of the image when changing frames depends on this speed.In order to make this parameter optimal, a voltage of maximum amplitude must be applied to the crystal.
Advantages and disadvantages of technology
Pros:
- Low power consumption - about 30 W/h. For example, CRT TVs consume 3 times more.
- During intensive work, heating should not exceed 30ºС. Screen burn-in is virtually eliminated.
- An anti-reflective coating is applied to the screen, which eliminates reflections, reflections, and geometric distortions.
- It is lightweight, has a thin screen - does not take up much space, and is mounted on a wall with a bracket.
- No harmful electromagnetic radiation, no harm to the eyes.
- The service life is, on average, twice as long as plasma. Then the lamp is simply replaced, not the screen itself.
- Screen sizes can range from miniature (wristwatch) to 100 inches.
Minuses:
- Primary colors suppress midtones and shades.
- There is a so-called trailing problem, a residual image.
- Great response time.
- Small viewing angle compared to plasma.
Some features
- Contrast. Modern technologies, due to pixel polarization, allow you to smoothly change brightness over a wide range of 0-90º. Therefore, LCD TVs display dark shades well and are easy to distinguish.
- Brightness. As noted earlier, polarization cannot change instantly; it takes some time. Therefore, TVs of this system have the problem of displaying a rapidly changing, dynamic picture.
- Limitation viewing angle. Due to the design of the LCD display, which looks like a multilayer sandwich, the viewing angle is limited. So, with some deviation of the eyes from the screen, the polarization angle and, accordingly, the brightness of the crystal changes. Color rendering and image contrast decrease.
- Broken pixels. Crystals do not break, so failure of the control transistor results in a dead pixel. The crystal, depending on the technology, can behave differently - if, in the absence of voltage, light does not pass through it, then the dot will be black; when the maximum flux passes through, it will burn.