Construction of a floor on the ground: how to design earthen floors
Floors on the ground are laid directly on the soil, which is thoroughly compacted, and then a layer-by-layer cake is formed. This simple technology can be implemented only if the groundwater in the area is low (maximum 4 m to the surface). Schemes of such a floor, as well as step-by-step installation instructions, can be found in the presented material.
The content of the article
Schemes and advantages of flooring on the ground
Flooring on the ground is the simplest design option, which is usually cheaper than others. It has several advantages:
- ease of installation - the screed can be completed literally in a day;
- good thermal and waterproofing (if high-quality concrete is used);
- durability, wear resistance;
- affordable price.
However, these advantages can only be achieved if you know the structure of the ground floor and certain requirements:
- dry, dense and motionless soil;
- groundwater reaches a height of no more than 4 m;
- mandatory waterproofing and insulation.
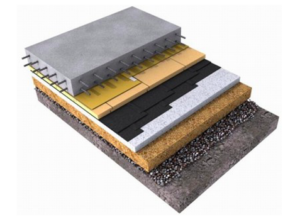
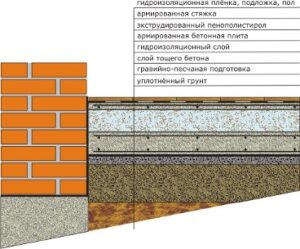
It is also necessary to imagine the “pie” - what the structure of the floor on the ground consists of:
- layer of compacted sand;
- crushed stone or gravel;
- waterproofing;
- concrete screed;
- steam and heat insulation;
- finished floor, finishing.
Before starting work, you will also need to calculate the floor based on the ground.It can be installed in any house that meets the requirements described above. In this case, they focus on a thickness of 35-50 cm. If, due to thermal insulation or the close occurrence of groundwater, it is necessary to make a thick embankment of 60 cm or more, the work will be too expensive. In such cases, it is advisable to simply lay a monolithic concrete slab - it will cost less.
It is also recommended to clarify the design diagram. If the composition of the floor on the ground is approximately the same, then the patterns may be different:
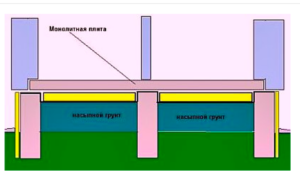
- with support on the ground;
- supported by walls.
In the first case, the screed is placed directly on the ground or on pre-installed wooden logs. This is the simplest and therefore inexpensive type of construction, providing normal thermal insulation even in severe winters.
But if the backfill is required too high (60-100 cm), such a flooring scheme on the ground will be too expensive. Therefore, it is better to choose the second option with support on the walls. Thanks to this, an air gap is created from below, and the resulting space can be used as a cellar. But such a design is more complicated, and the calculation of floors based on the ground shows quite high costs.
Step-by-step installation instructions
Earthen floors are installed in several stages - first, the base is prepared, the rough surface is finished, after which hydro- and thermal insulation is created, and then it is reinforced and filled with concrete.
Preparing the base
The technology for flooring on the ground at the first stage involves preparing the base. The procedure is as follows:
- Using a level, the zero point is determined.
- Carefully compact the soil surface - for this use a vibrating tamper.
- Sand is first poured a quarter higher than the calculated height.
- The layer is moistened and compacted - you can use either a vibrating tamper or a small roller.
- The next layer of the floor on the ground is gravel or expanded clay.

Arrangement of the subfloor
During construction, the thickness of the floor layers on the ground is observed. So, the compacted sand base should be approximately 200 mm, and the concrete layer should be 100-150 mm, as shown in the diagram.
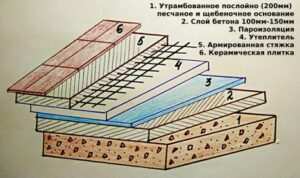
In this case, concrete is also used for the first layer of the subfloor. It is needed to level the surface for the purpose of subsequent laying a layer of waterproofing. Calculation of the floor slab on the ground shows that for this purpose it is better to use lean concrete B 7.5-10 with crushed stone fraction from 5 to 20 mm. Filling is carried out so that the resulting layer is 40-50 mm.

Waterproofing
Next you need to carry out waterproofing. To do this, it is not necessary to draw up a drawing of the floor based on the ground - an approximate drawing will do. The following are used as waterproofing materials:
- bitumen in a roll or polymer membrane - it is overlapped by at least 10 cm and fixed with construction tape;
- the insulating sheet is also overlapped and placed on the walls by at least 15 cm, after which the excess parts are cut off;
- If waterproofing is difficult to carry out, it is possible to pour a concrete base and then apply bitumen or polymer to it.

Insulation
Concrete is poured in such a way as to take into account the calculation of floors on the ground based on bearing capacity. Since the surface will experience static and dynamic loads, it is necessary to choose durable insulation, for example:
- extruded polystyrene foam - withstands high pressure, does not rot, is affordable;
- polystyrene foam classes PSB 35 (for residential premises) or 50 (for household premises - bathhouse, garage, shed, etc.);
- mineral wool is also quite durable and protects well from the cold, but can suffer from humidity, so it needs a sealed vapor barrier.
Floor constructions on the ground provide for the installation of insulation strictly as a vapor barrier. A dense PVC membrane is usually used as it. It is also overlapped and glued with tape. You can also use a bitumen membrane with fiberglass or polyester - it is more affordable, and is not inferior in strength to PVC.

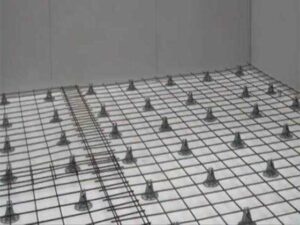
Reinforcement
The ground floor of the first floor must be reinforced with a mesh of rods, the diameter of which is 3-5 mm. Since this is not a classic foundation, one layer is enough, and the mesh must be laid taking into account the following rules:
- It is better to mount as close to the concrete surface as possible;
- The optimal layer thickness is 15-20 mm, so it is better to raise the mesh and place it on concrete or polymer pads.
- the perimeter of the structure is protected with exactly the same layer, for example, with cards with square cells of 10*10 cm.
Fill
We can say about the ground field that it is a multi-layer structure (pie), which ends with a damper layer and fill. At one of the last stages, strips of polyethylene are cut out, placed on an edge along the perimeter, or a special damper tape is glued to the bottom of the walls, as shown in the photo.

The base under the floors must be carefully leveled on the ground using plaster beacons, which are placed in the thickness of the gypsum solution. You can also use starting putty. The mixture is placed between the beacons and leveled using the rule. Next, the beacons are removed and the cavities are filled with concrete, after which the surface is leveled again.
Thus, all work can be done independently, since no special equipment is required.In this case, the quality of the tamper is of great importance - for this it is better to use a vibrating tamper and control the quality at the construction level.