Polypropylene or metal-plastic pipes: what are the differences and what is better for heating
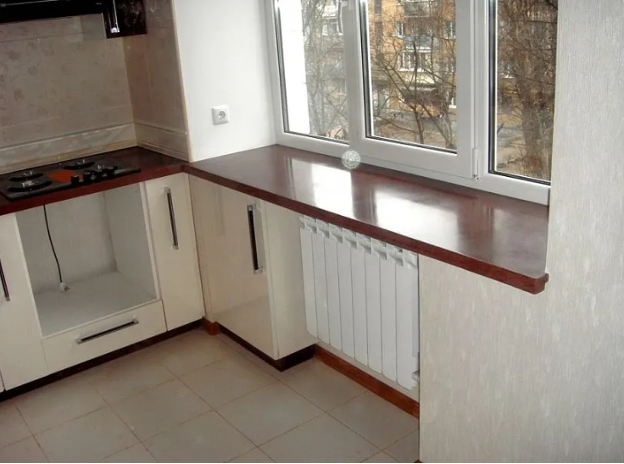
To create a heating circuit, polypropylene or metal-plastic is often considered. Both materials are similar because the composition is based on an organic polymer. But metal-plastic products have an insert made of foil or fiberglass, due to which they can withstand higher temperatures. A description of the advantages and disadvantages of both materials, as well as a detailed comparison of the main characteristics, can be found in this article.
The content of the article
Similarities and differences between materials
When considering which is better – polypropylene or plastic, you first need to understand exactly how they differ. Both pipes are made from the same organic polymer – polypropylene. The result is white products made of dense plastic, which are lightweight and have several advantages:
- absolute resistance to corrosion;
- resistance to contamination due to smooth internal walls;
- light weight and easy installation - using a soldering iron you can quickly build a pipeline of the required length;
- affordable price;
- convenient transportation.

But if you study in detail which is better - polypropylene or plastic, you can find several disadvantages of the material:
- can withstand temperatures only up to 70-80 degrees;
- expands significantly when heated, which can lead to deformation;
- is destroyed by prolonged exposure to open sunlight.
Metal-plastic is made of the same polypropylene, but in the middle it has a layer of aluminum foil or fiberglass. Thanks to this, such pipes are more resistant to heat (can withstand up to 90-100 degrees) and expand less when exposed to high temperatures. Therefore, it is quite obvious what is better for heating – polypropylene or metal-plastic.
However, polypropylene pipes have their advantages. They are more affordable, so they are in great demand. Such products are excellent for hot and cold water supply systems, where the circuit temperature is just within acceptable values (60-70 degrees). They can also be used to create an inexpensive country water supply system.
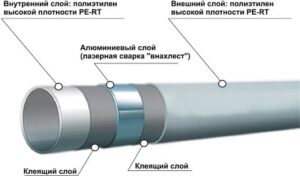
What is better for heating: comparison by parameters
The pros and cons of polypropylene pipes, as well as the compositional features of metal-plastic, allow us to draw a conclusion about which products are better suited for heating. To understand this issue in detail, it is necessary to make a comparison of the main technical characteristics.
Durability
If we talk about which pipes are better - metal-plastic or polypropylene, you can start with the most important parameter - durability. This indicator primarily depends on the resistance to high temperatures in the heating circuit.
On the one hand, metal-plastic will last longer thanks to a layer of aluminum foil or fiberglass. But on the other hand, it also has temperature limits of 90-100 degrees.However, in a heating system the indicator can reach 110 degrees, which is equally harmful for both metal-plastic and classic polypropylene.
When constantly exposed to high temperatures, the material expands greatly and deforms over time. Therefore, the service life is reduced from that declared by the manufacturer (50 years) by almost half - to 20-25 years. This problem is especially relevant for apartments where there is no way to regulate the temperature.
Installation method
To figure out which is better – metal-plastic or cross-linked polyethylene, you also need to evaluate the installation method:
- Polypropylene The products are heated on a soldering iron and joined together. Moreover, you need to hold them for a strictly defined number of seconds in order to prevent overheating and at the same time ensure the desired melting temperature. Also, the fragments are connected with fittings and adapters, which is somewhat more complicated compared to metal-plastic.
- Metal-plastic pipes are mounted only with fittings; a soldering iron is not used in this case. On the one hand, it is easier, but on the other hand, skills in working with press jaws are required. Instead, you can connect the elements with collets, but then you will need to periodically tighten them.

Number of connections
The difference between polypropylene pipes and metal-plastic pipes is also due to the number of connections during the installation process. The fundamental difference is that polypropylene is supplied in small fragments up to 2 m, and metal-plastic is supplied in coils of several meters.
Such products can be bent at small angles; a spring or lever type pipe bender is used. It turns out that the number of connections is much less for a metal-plastic circuit, which also facilitates installation.
Cross section on fittings
But metal-plastic also has a significant drawback - significant narrowing in metal fittings. For example, the pipe may be 3/4 inch in diameter, but the angle is only 1/2 inch in diameter. Therefore, in the event of an emergency, a pressure drop, it is these connections that are most vulnerable.
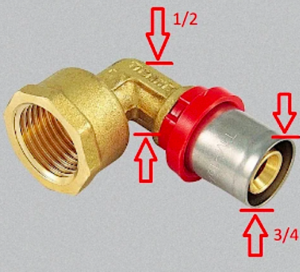
In the case of polypropylene, this disadvantage does not exist, since the diameters of the pipe itself and the fitting exactly match each other. Thus, metal-plastic wins on almost all counts, with the exception of the last one. But even despite this, it is more often used in heating systems than classic polypropylene.





