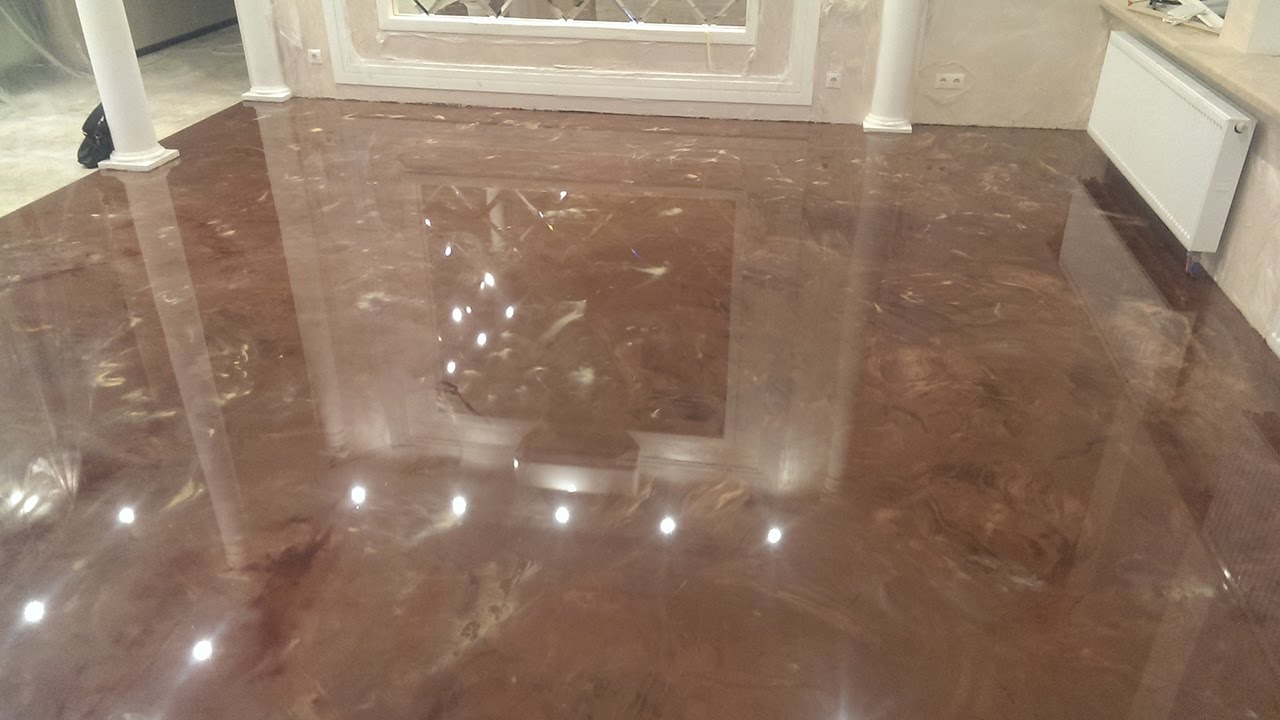
Thickness of underfloor heating for tiles
When creating a warm floor, it is necessary to take into account its thickness. If we make it small, there is a risk that the temperature will damage the material. But too thick is also bad. It will block the supply of the required amount of energy. It is important to choose the optimal solution.
The content of the article
What should be the thickness of a heated floor under tiles?
The following parameters depend on this indicator:
- System service life.
- How quickly the surface warms up.
- Uniform heating.
- How well does it hold heat?
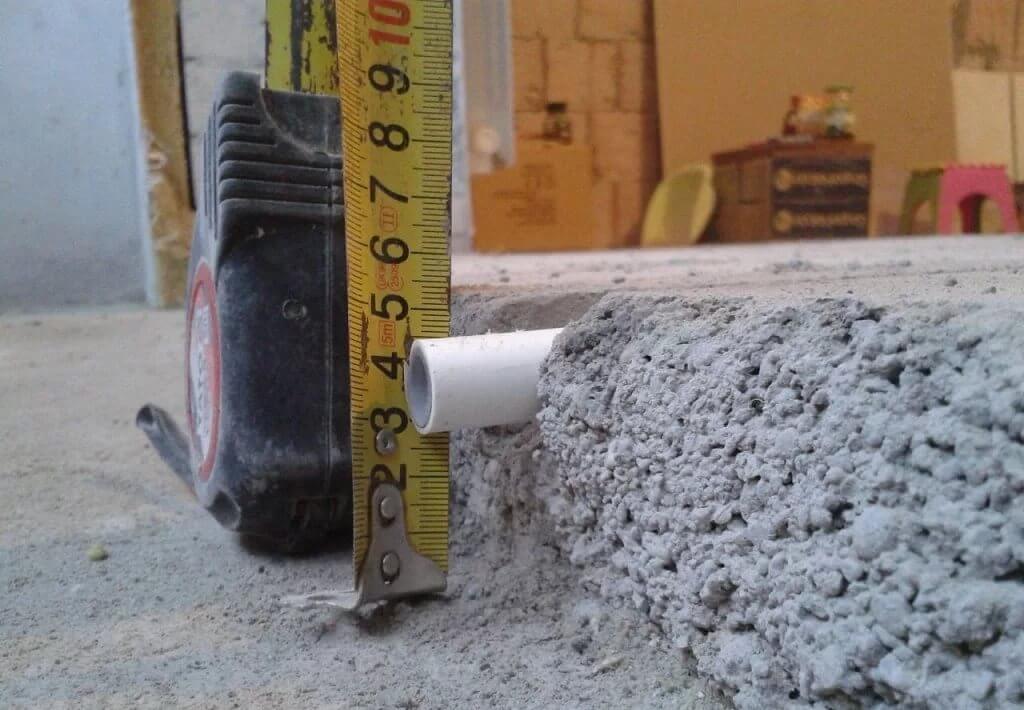

The thin layer heats up quickly, but with constant temperature maintenance, cracks begin to appear in the concrete. Most defects appear in those places where the pipes are located.
The minimum height of the screed layer is about 7 cm, but it is only suitable for tiles that can withstand overheating. The average pipe filling size is about 10 cm. This parameter is only suitable for floors in houses and apartments. And in warehouses or retail facilities, the layer height can be more than 25 cm.
The indicator also depends on the size of the pipes. Without thermal insulation, the figure will be about 5 cm.
Attention! With electric heating, the thickness requirements are not so high, since it is much easier to regulate the energy supply.
Thickness of underfloor heating layers
The heated floor consists of several layers. First, the screed is taken into account. It is mounted to the finishing field and tied to the base or foundation.But if the surface is insulated on the ground floor, the screed is done on the ground. The screed is a kind of pillow. Its average size is about 5 cm.
The next layer is insulation. It all depends on the chosen material. If you choose expanded polystyrene (it is the most common), its average thickness should be about 10 cm. But you can set the minimum - 5 cm. The density of the material is also taken into account. These figures are suitable if the density is about 30 kg/m3. For denser material, the thickness must be reduced.
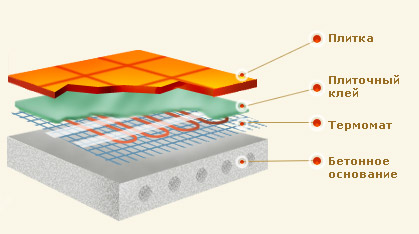
Then comes the plastic film. Its thickness is from 1.5 to 2 cm. A mesh of rods with a thickness of 0.4 cm is made on top of it. And after creating the reinforcement, you can solve the issue with the pipeline. The diameter depends on the material of manufacture. The average pipe thickness is 1.5 cm.
Now you need to cover the pipeline. An additional 2 cm of mesh is sufficient for this. The last layer is a screed, about 5 cm thick. It is not only the base, but is also responsible for heat accumulation.
By calculating the sum of all layers, we get the height of the total floor.
Deviation from specified parameters: consequences
If you make the floor too thick, the temperature will be lower than expected. The reason is poor thermal insulation. It can always be increased, but then more energy will be required. There may also be problems with regulating the system.

If the insulation is made too thick, a large amount of energy is lost when it passes through the insulation.
There are also cases when certain parts of the surface are warm and certain parts are cold (this applies to water structures). Most likely, the heat is poorly distributed. In a place where there are no pipes, energy does not flow to the coating. You can reduce this figure or install an additional pipe.
The last problem is that if you make the insulation layer very thin, there is a risk of damage to the screed.