What is a light bulb, design and principle of operation
Have you ever wondered what a regular light bulb is? Most of us know that the simplest lighting device consists of a base, a bulb and a tungsten filament, but how does it function, why does it burn out over time, and why are lamp bulbs filled with inert gases?
We will talk about all the characteristics of simple “Ilyich bulbs” and modern fluorescent and LED devices in this article.
The content of the article
What is an incandescent light bulb
An ordinary incandescent lamp is a powered light source, the main part of which consists of a refractory material that acts as a filament body. In most cases, such material (conductor) is placed in a vacuum flask or a flask filled with inert gases. When current passes through a conductor, it heats up and begins to emit a bright glow.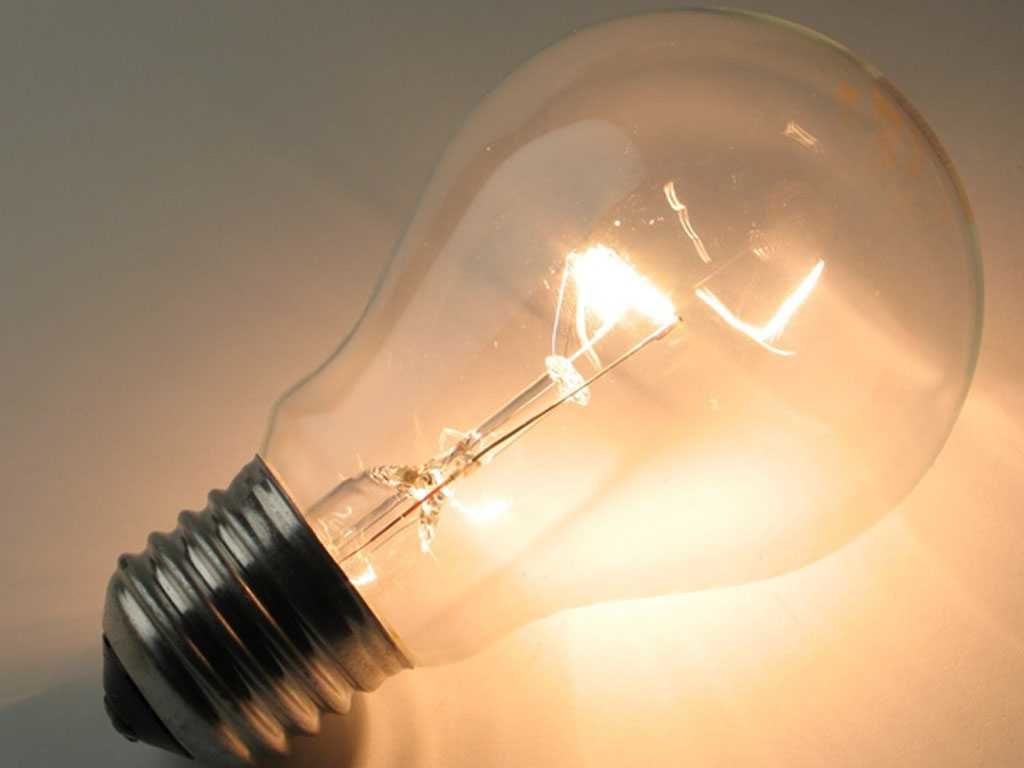
Interesting! In order for the tungsten filament of a light bulb to light up, it must be heated to a temperature of about 2000 °C. The incandescent temperature limit can be considered to be 3410 °C.
History of creation
In fact, no scientist has ever invented anything entirely on his own: this is what happened with the “classic” light bulb. Back in 1840, a British inventor named Warren De la Rue designed the first incandescent lamp powered by a platinum conductor. Two years earlier, in 1838, a Belgian scientist named Jobard invented the world's first carbon-core light source. Well, exactly a hundred years before the end of World War II, Heinrich Goebel creates the first prototypes of modern light bulbs.
It is noteworthy that Goebel's first lamp had a charred bamboo thread placed in a vacuum. The scientist continued to work on his brainchild for about 5 more years, after which he presented it to the general public.
Russian scientists also made a significant contribution to the invention, which is now used by the whole world. Thus, in 1874, the first light bulb with a carbon core placed in an airless environment was registered in the name of Alexander Nikolaevich Lodygin. The big problem with such a light source was that carbon as a conductor could not last long enough and burned out soon after use. Over time, the bright minds of the planet came up with the idea of replacing coal with tungsten.
Interesting! When we talk about electricity and lighting devices, we cannot fail to mention the great Thomas Edison. It was he who first created and patented an incandescent lamp that was cheap to produce and durable (relative to most devices of that time).
Since its invention, the familiar light source has not changed much, but technical changes still took place in it: the conductor was replaced with a more advanced one, and the space inside the bulb began to be filled with a special gas.
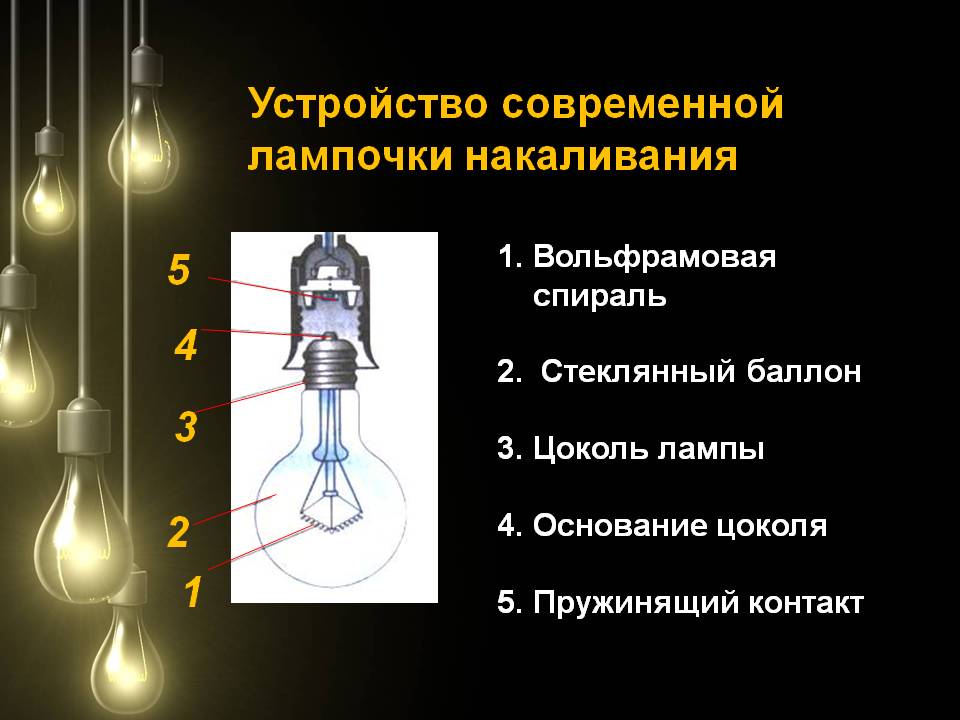
Design features and principle of operation
Standard LN consists of:
- a flask filled with an inert gas (or devoid of air at all);
- a base that simultaneously serves as both a “lid” of the bulb and an element for connecting the lamp to the network;
- electrodes;
- filament coil located on special supports;
- base contact.
Tungsten was chosen as the conductor material in order to minimize current consumption for heating and reduce the cross-section of the filament to the minimum possible.
Interesting! The resistivity parameter of tungsten is three times greater than that of copper.
The spiral is powered by current from the electrodes, and molybdenum is used as the main material of the “horns” on which the spiral is installed: it is refractory and does not actually expand when heated. The use of an inert gas increases the potential service life of the spiral: in a gas environment it is “more difficult” for it to burn out. As for the base, its size and threads on it may vary.
Characteristics and types
In addition to the usual household drugs we are used to, experts identify several more of their varieties, including:
- Decorative. They are distinguished by non-standard bulb shapes, an enlarged spiral and low lighting. Such devices are most often used by designers to implement projects in the “vintage” style.
- Illumination. They have a bulb painted on the inside and have low power (up to 25 W). They quickly change the shade of the glow, so they require frequent replacement.
- Signal. Previously, they were widely used in various lighting devices, but today in this area they are being actively replaced by LED options.
- Mirrored.The bulb of such a lamp is partially covered with a layer of aluminum that reflects light well, which allows it to concentrate the lighting on a certain point in the space of the room.
- Transport. They are used to equip the optics of cars, tractors, airplanes, various marine vessels, etc. They have increased strength and are resistant to vibration.
- Double strand. A special subtype used in railway traffic lights, airplanes and cars.
Reference. There are other types of LN, but today most of them have been replaced by more modern devices, which will be discussed a little further.
Advantages and disadvantages
The positive qualities of classic LP include low cost, small dimensions, immunity to small voltage drops in the network, a pleasant spectrum of illumination for human vision, a wide range of power options, the absence of toxic or other harmful components in the composition and noise in operation. If we talk about the disadvantages, then among them it is worth mentioning a relatively short service life, a fairly high current consumption and a fire hazard.
Important! The surface around powerful incandescent lamps can heat up to +330 degrees Celsius. Be careful!
Scope of application
Classic LNs are used for household lighting of premises and local areas, commercial real estate, used in automobile, railway and air transport, installed in portable lighting devices (pocket flashlights, etc.), used in cinema, design, medicine and many other sectors of life.
Design and principle of operation of modern types of lamps
Modern lighting devices include halogen, fluorescent, energy-saving and LED devices. Let's consider each type individually.
Halogen
Such devices are a modernized version of classic LNs. The flask of such a device is filled with halogen, which reacts with tungsten that evaporates as it heats up. This allows you to extend the life of the device. In addition, quartz is used in halogen lamps. Halogen lighting devices usually have higher performance characteristics than conventional lamps.

Luminescent
These devices are also called fluorescent lamps. They have high color rendering quality, which allows them to be used in lighting shop windows and shelving. Compared to LN, a luminescent device consumes 4–5 times less energy and has a longer service life. They also have their drawbacks - poor performance at low temperatures and the content of harmful substances (including mercury) in some models.
Energy saving
The main feature of energy-saving lighting devices is the electronic unit, which ensures both the ignition and operation of the lamp. Such a device is characterized by more stable operation, lower power consumption, longer service life and a wide range of available colors.
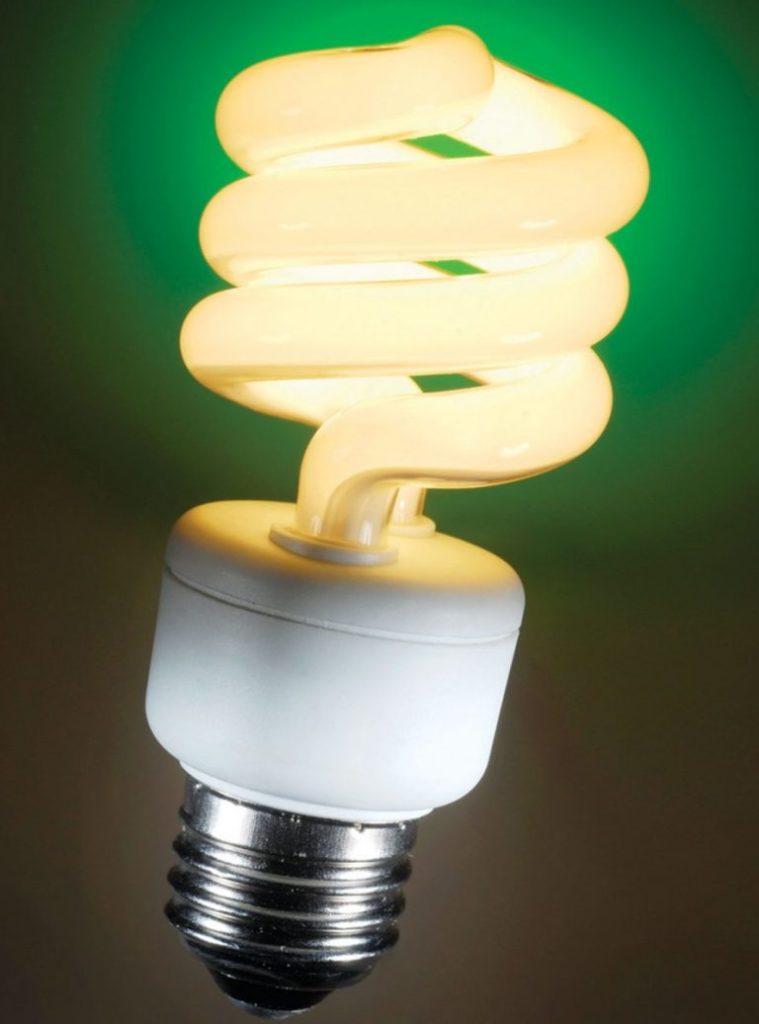

Important! In the production of energy-saving lamps, substances hazardous to nature and humans are used, so their disposal must be carried out exclusively through special collection points.
LED
The design of such lamps uses semiconductor crystals: they create a glow when electric current passes through them.Compared to the same halogen devices, LED devices are approximately 4–7 times more efficient, and in terms of service life such a device can last up to 50,000 hours. The only drawback of LED lamps is considered to be their high cost, however, taking into account the savings on maintenance and consumption, in the long term it is much more profitable to purchase them.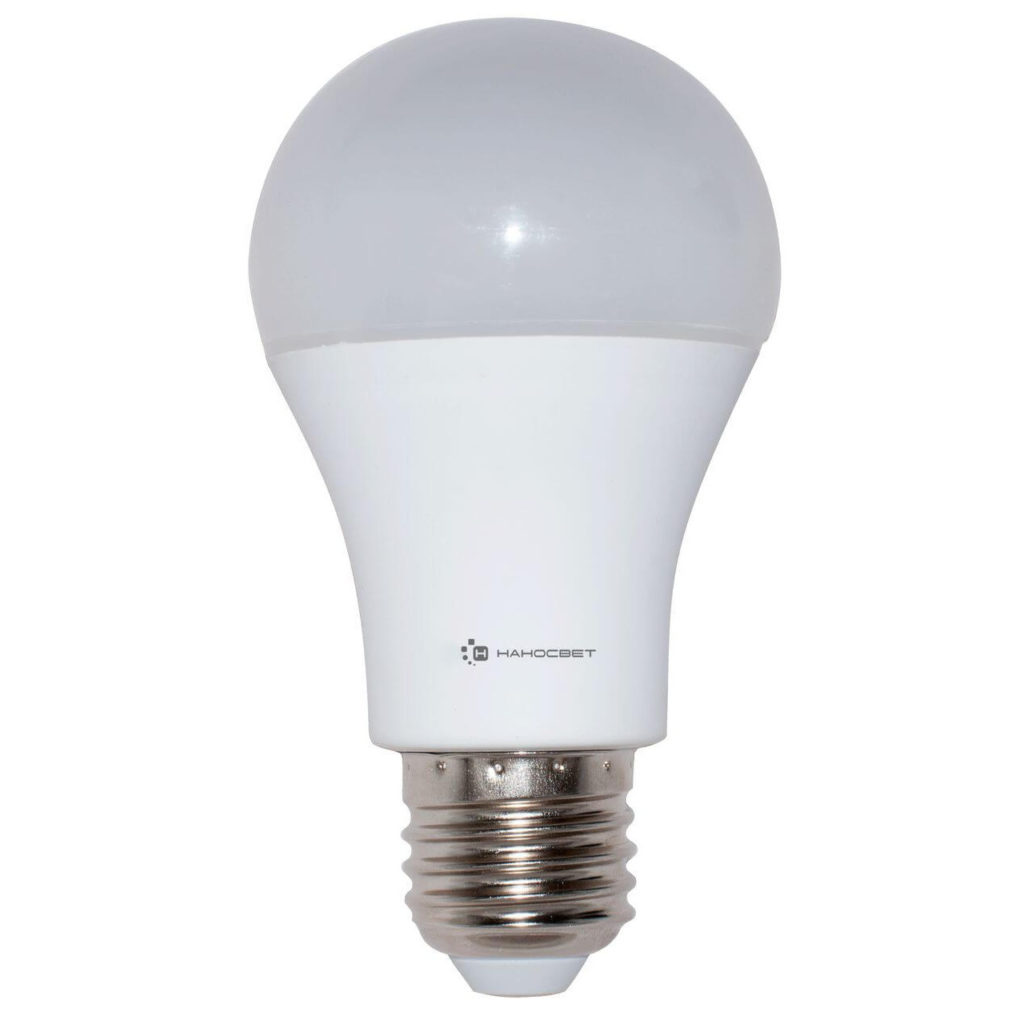
So we found out what a light bulb is, looked at most types of modern and not so modern options. We hope that now you have a general idea of the features of their operation.





