How to choose contact lenses
 The need for vision correction is becoming increasingly in demand in modern society. There are reasons for this - both quite objective (poor nutrition, poor environment, the need for constant eye strain at work, injuries and diseases) and subjective (unhealthy lifestyle, ignorance or unwillingness to comply with preventive procedures, for example, therapeutic exercises for the eyes) .
The need for vision correction is becoming increasingly in demand in modern society. There are reasons for this - both quite objective (poor nutrition, poor environment, the need for constant eye strain at work, injuries and diseases) and subjective (unhealthy lifestyle, ignorance or unwillingness to comply with preventive procedures, for example, therapeutic exercises for the eyes) .
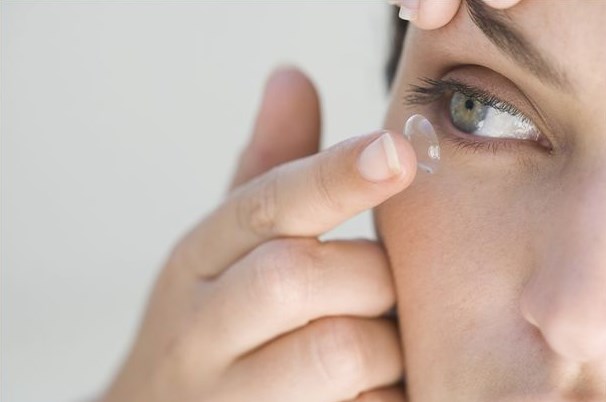
Contact lenses are the most common method, successfully competing with glasses in terms of efficiency and having a number of advantages - comfortable wearing, attractive appearance, full viewing angle, etc. But they are not suitable for medical reasons for everyone, they require painstaking care, and most importantly - careful selection.
The content of the article
Selecting Contact Lenses
Can I choose it myself?
 It is more than risky to try to independently find the best option for yourself - especially if you have not previously had the slightest experience in wearing corrective lenses. The prescription for glasses cannot in any way be the basis for choice - they have fundamentally different parameters.
It is more than risky to try to independently find the best option for yourself - especially if you have not previously had the slightest experience in wearing corrective lenses. The prescription for glasses cannot in any way be the basis for choice - they have fundamentally different parameters.
To make the right choice, which will not entail further deterioration of vision or dry eye syndrome and can have a therapeutic effect, a special consultation with an ophthalmologist is required.
How lenses are selected
A number of criteria that are vital for proper lens operation, comfort and eye health can only be determined by a specialist:
- To select, you need to take into account an additional parameter - base curvature cornea. It can only be measured by an ophthalmologist with a special instrument - a keratometer.
- In some cases, even this study may not be enough and the data is clarified by computer diagnostics: aberrometry or keratotopography. It is obviously impossible to determine the correct value on your own - and lenses without it simply will not be sold to you (at least by responsible and decent people);
- The size of the eye (respectively, the size of the lens) is calculated using a special measurement or based on the same tests;
- Vision correction with lenses has a significant limitation - insufficient tear production, which is determined by a separate analysis (Schirmer test). In this case, it is only possible to use silicone hydrogel options (with certain reservations);
- Glasses are located at some distance from the eyes (about 12 mm), while lenses are practically on the surface. Consequently, discrepancies begin (small optical power correction is required).
After all the necessary research and calculations, the ophthalmologist provides a trial model for fitting.All samples are taken again to make sure that the eye has acquired the required visual acuity and feels comfortable (if the pain is too strong or does not stop for more than 5 minutes, your eyes are too sensitive to this type). Only after this is a separate prescription issued with updated and supplemented data.
Important: Save prescriptions after purchase - this is a convenient and reliable way to track the dynamics of all changes in the functioning of the eye and objectively assess the effectiveness of treatment.
Which is better: lenses or glasses?
 As a way to maintain visual acuity, they are not inferior to each other in effectiveness; read the differences in the following points:
As a way to maintain visual acuity, they are not inferior to each other in effectiveness; read the differences in the following points:
- Wearing comfort: lenses do not in any way limit a person leading an active lifestyle - on the other hand, glasses are easy and quick to take off and put on;
- Aesthetics: lenses will be the optimal choice for people who tend to hide the condition of their vision from others. It is worth considering that well-chosen glasses will fit into a certain style and help hide some imperfections, for example, correct the symmetry of the face;
- Cost and care — glasses are cheaper, last longer and are easier to care for. If you forget to place the lens in a special storage solution on time, it can no longer be restored.
The clear advantages of contact lenses are no fogging during temperature changes, full peripheral vision (ophthalmologists themselves believe that its absence stimulates atrophy of the eye muscles and further deterioration of vision), a certain psychological and practical comfort.
Attention: It is worth remembering that under no circumstances should you use lenses if you have glaucoma, infectious inflammation of the eye (for example, conjunctivitis or blepheritis) and diseases associated with a serious decrease in immunity (tuberculosis or AIDS), diabetes mellitus, acute sinusitis, severe allergic reactions.
Types of contact lenses
What influences the choice of lenses?
There are many manufacturers on the vision correction market offering a wide range of different lenses, the selection criteria of which can confuse not only a beginner. Depending on their purpose, material of manufacture and processing method, mode of wearing and estimated frequency of replacement, several classifications can be distinguished. In each specific case, the service life, specific purpose, cost and conditions for wearing the instrument are determined.
More detailed article about types of contact lenses.
Hardness degree
 The design can be soft or hard. The hard structure of the first has a more pronounced therapeutic and prophylactic effect, they are stronger and will last longer than the soft ones. There is no need to constantly wet the surface with moisturizing drops. But adaptation to them occurs over a longer period of time (there may be some discomfort for another week), the shape of the cornea may change (the so-called keratoconus), and the price is slightly higher.
The design can be soft or hard. The hard structure of the first has a more pronounced therapeutic and prophylactic effect, they are stronger and will last longer than the soft ones. There is no need to constantly wet the surface with moisturizing drops. But adaptation to them occurs over a longer period of time (there may be some discomfort for another week), the shape of the cornea may change (the so-called keratoconus), and the price is slightly higher.
Soft lenses are less effective at correcting vision defects and are more likely to fail - the fragile material breaks easily and causes regular trouble during maintenance (mandatory exposure and storage in a disinfectant solution). Advantages: simple and affordable replacement of worn-out instruments, a wide variety of colors and camouflage of eye defects (for example, eyesores).
Material
Corneal cells are not connected to the circulatory system and are supplied with oxygen directly from the atmospheric air. Therefore, such an important characteristic of the material as gas permeability arises - how well air passes through. Lack of oxygen leads to severe pathologies, swelling, ulcers and keratitis.
Another important property of the base for a future lens is that foreign organic components are better retained on some surfaces. These can be waste products of microorganisms living in the eye cavity, fatty and protein elements in the composition of the eye.eh, metabolic results removed through the lacrimal eyes (this becomes especially noticeable in smokers - the lens turns yellow over time from nicotine). Materials with higher ionic potential are more susceptible to retaining such debris, which can cause mucosal irritation and impair vision.
 Any lenses are made from complex polymer composites with high biological compatibility. The two most common options are pure hydrogel (hydroxyethyl methacrylate, also known as HEMA) or combined with silicone. The first method provides clear vision without allergic side effects and discomfort, but practically does not allow oxygen to pass through. The minus lens dries out quickly and is poorly prepared for long-term wear - regular overexposure leads to serious consequences (hypoxia leading to severe swelling of the eye).
Any lenses are made from complex polymer composites with high biological compatibility. The two most common options are pure hydrogel (hydroxyethyl methacrylate, also known as HEMA) or combined with silicone. The first method provides clear vision without allergic side effects and discomfort, but practically does not allow oxygen to pass through. The minus lens dries out quickly and is poorly prepared for long-term wear - regular overexposure leads to serious consequences (hypoxia leading to severe swelling of the eye).
 Silicone hydrogel are highly popular due to their low moisture content (regular wetting is not necessary) and optimal oxygen access - it becomes possible to wear them for a long time without side effects.
Silicone hydrogel are highly popular due to their low moisture content (regular wetting is not necessary) and optimal oxygen access - it becomes possible to wear them for a long time without side effects.
Separately, it is worth noting the American classification standard of the National Committee on Drugs and Food Additives (FDA), in which all materials are divided into 4 groups based on their ability to adsorb water and foreign protein deposits:
- Group 1: non-ionic polymers with low water content (up to 50%);
- Group 2: nonionic polymers with high moisture content (over 50%);
- Group 3: low content ionic polymers;
- Group 4: ionic polymers with high water content.
More detailed article about the material and composition of contact lenses.
Size and shape
 The lens can be positioned on the eye in completely different ways and, as a result, have a different size. Depending on the diameter, three groups are distinguished:
The lens can be positioned on the eye in completely different ways and, as a result, have a different size. Depending on the diameter, three groups are distinguished:
- Corneal (from 9 to 11 mm). Their distinctive feature is that the lens does not rest against the mucous membrane surrounding the eye, but is held in place by the surface tension of a thin layer of tears directly on the cornea. This type is especially well tolerated by patients with hypersensitivity and allergies and can even be prescribed to children.
- Corneoscleral (12–15 mm). An expanded version of the cornea, extending onto the sclera. The format is rapidly gaining popularity because, along with all the advantages of its small size, it shows good effectiveness in correcting many visual impairments.
- Scleral (up to 21 mm). Historically, the first version of contact lenses, with two layers - a visual one in the center and a haptic support part at the edges. It is held on the sclera, resulting in a gap between the cornea and the material. Currently, the method is not widely used, although it shows impressive therapeutic results.
The shape is completely determined by the tasks that the use of lenses must solve. Thus, spherical ones correct the consequences of myopia (myopia) and hypermetropia (farsightedness), aspherical ones have a more advanced design (the front part is made in the shape of an ellipse), which can further increase the contrast and clarity of vision, toric ones are an effective tool in the fight against astigmatism.
Attention: Multifocal lenses stand apart - with alternating hard and soft layers, which gives an equally good and clear view of objects at different distances. The number of layers proportionally determines the smoothness of the transition between near and distant plans - the most famous are bifocal layers with two clearly defined zones.
Wearing mode
The eye and sclera are extremely vulnerable areas of the body where pathogenic microorganisms quickly develop, dirt, biological secretions and small debris easily collect, and even a minor scratch can have serious consequences for the performance and well-being of the entire body. Continuously wear a lens in the eye only for a strictly defined period specified by the manufacturer. Depending on the composition and form, these may be:
- Daytime wear (daily wear, DW) — which must be removed at night and stored in a special disinfectant solution;
- Extended wear (EW) - can remain in place for up to a week without removing. After this period, it is necessary to give the eyes a rest, and the mucous membrane the opportunity to cleanse itself.
- Flexible wear (FW) - daytime, with increased characteristics and safety, allowing you not to take them off for a night or two on occasion.Sleeping in this way will not harm the eye as much as a daytime lens would;
- Continuous wear (CW) — up to 30 days of continuous operation. The starting material can be exclusively thin silicone hydrogel polymers that are highly permeable to oxygen.
In addition, any contact lens has its own full service life, which is strictly limited by the properties of its material and production features. Using an excess limit is a big mistake, leading to new severe vision problems and aggravation of existing ones.
The lifespan of traditional ones is up to a year. In reality, they are often worn until they become completely unusable or lost (by analogy with toothbrushes, the recommended period of possible use of which is also strictly limited).
Planned replacement (frequent replacement) imply updating in each new quarter of the year. Some types (disposable) designed to be replaced once a month or even more often - every 2 weeks. The idea of a planned replacement turned out to be so successful that today it is the most common production method and most large ophthalmological companies have already completely stopped producing traditional models.
One-day wear (one day) They are as safe as possible for health, are great for occasional wear and do not require maintenance at all - after wearing them for less than a day, the patient throws away the waste material. The downside is significant costs, even taking into account the lack of need to purchase care products.
Rules for care and wearing
Mandatory medical control
The task of an ophthalmologist is not only to conduct examinations and prescribe an adequate method of vision correction with fitting samples.The patient's vision condition should be periodically monitored, which will reveal the dynamics of the disease and allow an adequate response to it (for example, replace the lenses with others with precise parameters).
Important: Doctors themselves strongly recommend undergoing a preventive examination 1, 3 and 6 months after the start of wearing - this is how the degree of adaptation to vision correction is determined as correctly as possible and possible problems are identified. Next, you should regularly visit an ophthalmologist at least once a year and monitor changes.
Recommendations for use
- Contact lens hygiene rules ensure healthy and safe wearing throughout the entire lifespan. The doctor who prescribed the lenses is obliged to give a brief instruction to the patient on how to properly use and care for the lenses; they will also tell you in the store. Some of them:
- Do not touch lenses (worn or removed) with dirty, oily hands. Each time you need to first thoroughly wash your hands with simple, unscented soap;
- Women should remember that makeup is applied after putting on lenses. It is recommended to use non-fat-based cosmetics - this may damage the surface;
- The blister in which the new lens is stored must be hermetically sealed; damaged packaging automatically means a defect. The same applies to crumpled, wrinkled and damaged lenses - they cannot be used;
- Washing and lens storage is carried out exclusively in a closed container with a special disinfectant solution for at least 4 hours. Tap water can lead to the most unexpected consequences.
More detailed article about contact lens care.
Marking: symbols on the packaging and the lens itself
The packaging contains symbolic information telling the buyer about:
- Base curvature of the lens in mm (BC);
- Dimensions in mm (DIA);
- Optical power in diopters (D, as an option PWR);
- Material thickness in the center (CT);
- Shelf life (Exp.);
- Sterility of the product (STERILE);
- Sales are by prescription only, in accordance with FDA requirements (RXOnly).
Conclusion
Contact lenses are a rather complex vision correction instrument that requires careful and caring treatment. Sloppy and sloppy people should think seriously before purchasing - after all, careless maintenance of lenses will not only add hassle, but is also dangerous to health.
The doctor should select contact lenses for the patient. Too many factors that can only be measured with special equipment in laboratory conditions must be taken into account. If all the rules are followed and the instrument is carefully selected, you can count on real improvement and optimization of vision. Today, good contact lenses are recognized as the most effective and popular therapeutic means of solving vision problems.