Pros and cons of an infrared heater
 Infrared heaters are becoming increasingly popular nowadays. This is facilitated by the affordable price and high efficiency of the devices. How do such devices work, what are their technical characteristics, as well as their advantages and disadvantages?
Infrared heaters are becoming increasingly popular nowadays. This is facilitated by the affordable price and high efficiency of the devices. How do such devices work, what are their technical characteristics, as well as their advantages and disadvantages?
The content of the article
Operating principle of the IR heater
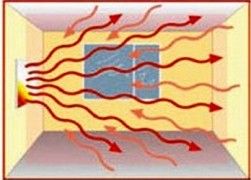 The operating principle of any heating device is based on the transfer of thermal energy from more heated bodies to less heated ones. The greater the temperature difference between the body and the environment, the more intense the heat exchange occurs.
The operating principle of any heating device is based on the transfer of thermal energy from more heated bodies to less heated ones. The greater the temperature difference between the body and the environment, the more intense the heat exchange occurs.
There are three types of thermal energy transfer:
- thermal conductivity;
- convection;
- radiation.
In fact, any heating device releases energy in all of the above ways; the differences are only in the percentage ratio between them.
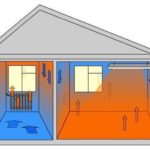
Traditional heating devices (oil heaters, heating radiators) provide the main transfer of heat flow due to convection. The heat of the device heats the layer of air in contact with it, which becomes lighter and rises, making room for heavy cold air, creating natural circulation in the room. Thus, the heating of surrounding objects does not occur directly, but through heated air masses. At the same time, the temperature near the ceiling is always several degrees higher than on the floor of the room.
Infrared heaters provide the main heat transfer by emitting infrared waves. The emitted waves easily pass through the air and are absorbed by solid surfaces, directly heating them. In simple words, an IR heater is a small artificial sun for your home. Spreading freely in space and hitting surfaces and people in the room, infrared rays heat them and these surfaces themselves begin to work as heat sources.
With this method of energy transfer, an unnecessary link - air - is eliminated, which can significantly increase the efficiency of energy use and ensure a more uniform distribution of heat in the room.
REFERENCE! Heaters that transmit more than 70% of energy through radiation are considered infrared.
Pros and cons of an infrared heater
To answer the question whether you need an infrared heater, you need to know all the advantages and disadvantages of devices of this type. The advantages of an IR heating system are:
- ease of installation and no need for maintenance;

- quick heating of a room of any size, you will feel a pleasant warmth immediately after turning on the device;
- the ability to create several thermal zones within one room;
- economical compared to traditional types of heaters;
- silent operation due to the absence of moving elements;
- do not burn oxygen and do not emit foreign odors;
- high fire safety (subject to operating rules), can be used in wooden houses;
- Possibility of use in wet areas.
IR heaters are not without some disadvantages:
- higher cost compared to traditional models;
- harmful effects on furniture and interior items (interior items and paintings that are constantly in the zone of action of short-wave infrared radiation lose moisture, as a result cracks may appear on them);
- the possibility of causing harm to human health if operating rules are not followed.
Scope of application of IR heaters
Contrary to popular belief, IR heaters are used not only in residential and office premises. Depending on the design, infrared devices are used in such areas as:
- agriculture, for heating greenhouses, young farm animals and birds;
- production, for main or local heating in workshops, hangars, garages;
- service sector, for heating outdoor cafes and restaurants;
- medicine, for disinfecting premises;
- industry, production of infrared saunas and heating furniture.
Industrial and household heaters are completely different devices; they differ both in the type of heating element (wavelength of infrared radiation) and in the type of energy source used
Types of infrared heaters
There are many types of infrared heaters. In fact, a surface heated above 60°C already intensely emits IR waves. In this case, the wavelength is inversely proportional to the surface temperature. Infrared is radiation with a wavelength from 0.74 micrometers to 1 millimeter. This range lies between the red end of the visible spectrum and the invisible part of microwave radiation.
IR devices can be classified according to several criteria. By energy source used:
- electric (to create IR rays, the heating element can heat up to 900 degrees, usually designed for an area of up to 25 square meters);
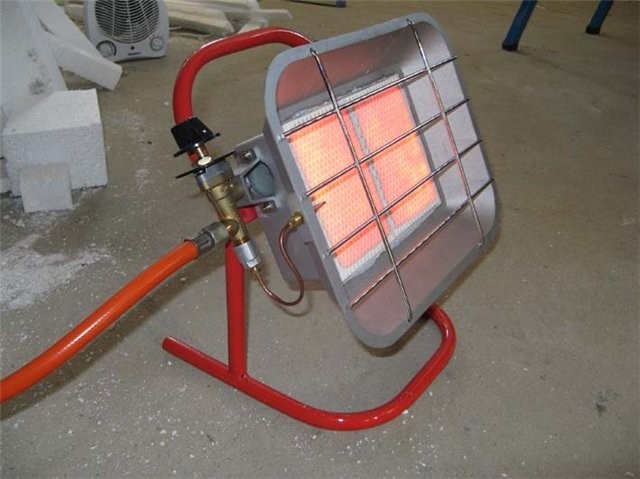
- gas (effective for heating large areas - hangars, gyms, greenhouses).
By type of heating element:
- Tube (got their name because of the bright golden glow during operation. The heating element is a filament made of chromium-nickel alloy or tungsten, placed in a quartz tube from which air is evacuated. Due to the high temperature, it emits short-wave radiation that can be harmful to human health, not recommended for residential premises).
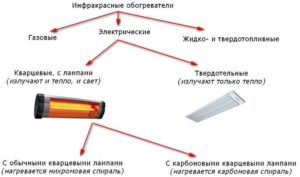
- Carbon (similar in design to lamp devices, the only difference is in the material of the heating element - they use a carbon or carbon spiral, which has a lower heating temperature, as a result of which these heaters emit longer waves that are safe for humans, the heating becomes softer and more comfortable).
- Ceramic (a large area ceramic panel acts as an element emitting infrared waves. The panel is heated to a temperature of about 60°C by a built-in metal spiral. The emitted IR spectrum is soft, safe and comfortable for humans, and the high performance properties of ceramics allow the use of these devices in educational institutions and wet environments).
- Micathermic (similar in structure and radiation spectrum to ceramic ones. The emitting element is a plate coated with metal oxides and a mica shell; heating is provided by a filament made of chromium-nickel alloy.The main difference from ceramic heaters is the lower heat capacity of the heating element and, as a result, a higher infrared effect).
- Film (the most modern sources of long-wave infrared radiation. They are a film no more than one millimeter thick. Film heaters can be placed under interior decoration elements on walls, floors or ceilings. They are an excellent source of distributed soft infrared radiation).
Heaters are also divided by wavelength:
- shortwave (designed for heating non-residential premises, IR radiation with a wavelength of 0.74...1.5 microns, characteristic of radiating elements with temperatures from 600 to 1000) ° C;
- long wave (provide softer heating intended for residential premises, characteristic of radiating elements with temperatures up to 120°C).
The most widespread at the moment are electric infrared heaters based on micathermic panels, lamp and carbon radiating elements.
What criteria should you consider when choosing a heater?
In order for the purchased infrared heater to fully realize its strengths, it is important not to make a mistake in choosing the type of device. Before choosing an infrared heater, you need to clearly determine for what purpose you plan to use it. Experts recommend adhering to the following principle:
- for additional heating of living rooms, use low-temperature panels (ceramic or micathermic);
- use devices with a surface temperature above 120 °C based on carbon elements as the main source of heat in office premises;
- To heat large areas, use high-temperature electric or gas heaters located at the distance from people recommended by the manufacturer.
It is worth carefully studying all the possibilities and making the right choice of a device that will bring radiant heat to your home.