Operating principle of a condensing boiler
 Recently, in Europe, concerned about the preservation of natural resources and the environment, the use of direct combustion gas boilers has been universally banned. At the same time, it is prescribed to install condensing-type units as more environmentally friendly and economical. Let's try to figure out what they are and how they differ from the gas heaters we are used to.
Recently, in Europe, concerned about the preservation of natural resources and the environment, the use of direct combustion gas boilers has been universally banned. At the same time, it is prescribed to install condensing-type units as more environmentally friendly and economical. Let's try to figure out what they are and how they differ from the gas heaters we are used to.
The content of the article
How does a condensing boiler work?
The water heating system of a private house works by burning the coolant and heating the heat exchangers. In a classic gas boiler, natural gas heats water in the heating circuit, and its combustion products are eliminated through the chimney. At the same time, water vapor is also formed along with carbon monoxide. It was the use of this steam to obtain additional heat that formed the principle of operation of condensing boilers.
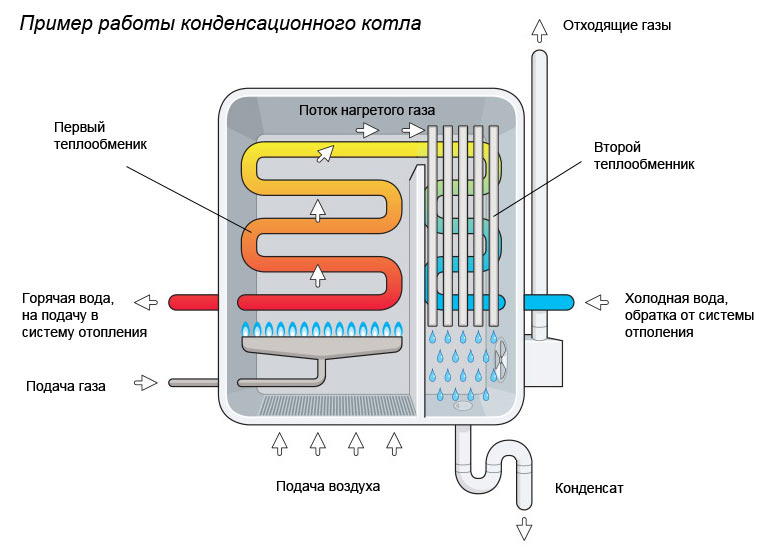
To obtain additional heat, special metal containers are installed where water vapor reaches the dew point and turns into liquid. At the same time, it transfers its heat to the heating system.
What does a condensing boiler consist of?
The design underlying condensing boilers was developed quite a long time ago, back in the last century. Its implementation was hampered by the lack of metals capable of withstanding high temperatures and humidity.Modern science has been able to create metal sulimin. It is able to withstand chemically active water vapor and withstand many condensation cycles.
On a note!
Sulimin is an alloy consisting of silicon and aluminum
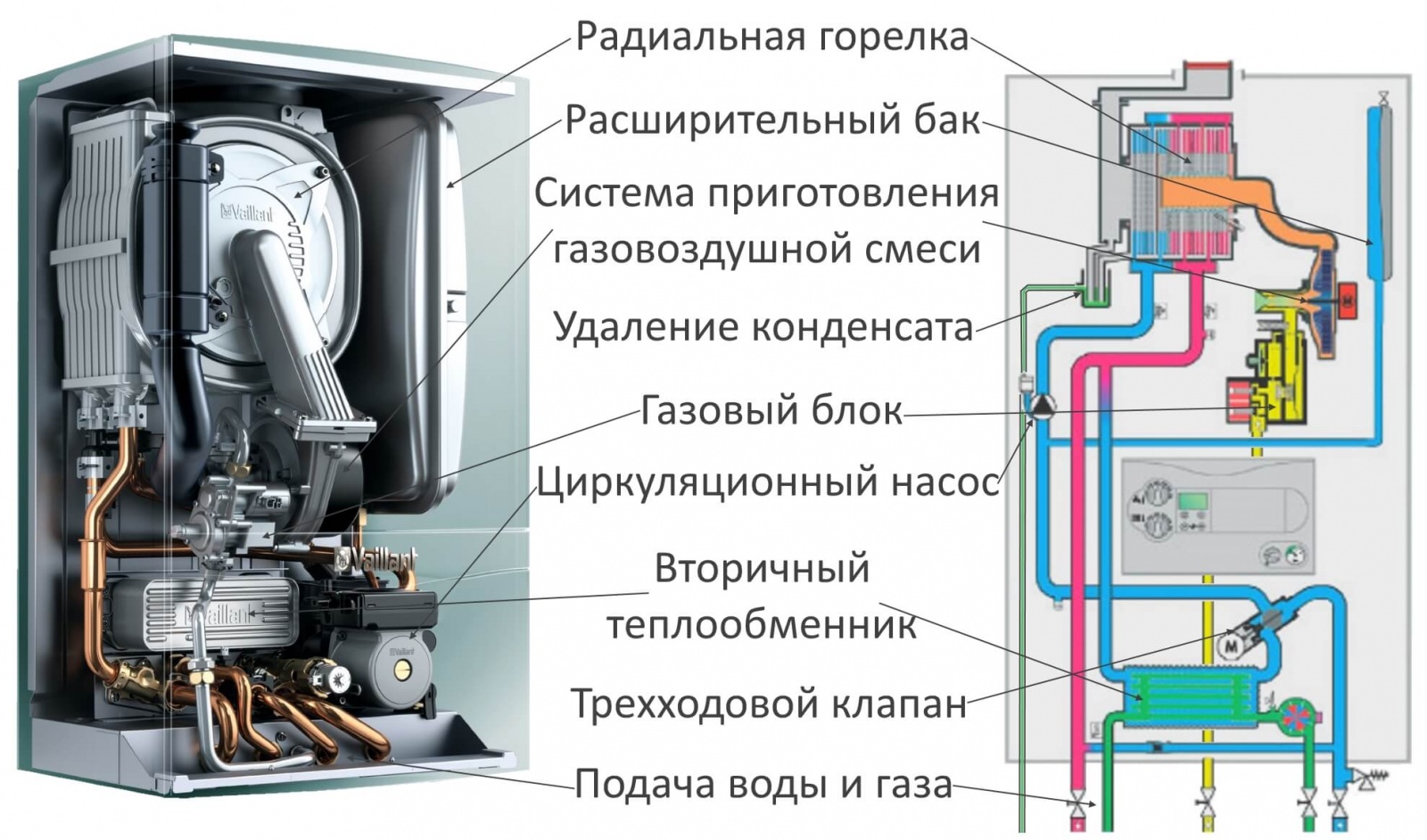
The structure of the boiler with a condenser is extremely simple:
- the body contains the familiar gas combustion chamber;
- Together with it, a system for collecting water vapor, condensing it and removing liquid is installed.
Oddly enough, such boilers are no more massive than classic ones, but their power is several times higher. The difference in gas consumption in spring and autumn is especially noticeable. At this time, you can save up to 20% of the coolant for heating the room.
In winter, the difference is noticeable only when using condensing boilers with underfloor heating systems, but with heating radiators the consumption will not be much different.
Rules for working with a condensing boiler
 Condensing-type boilers were developed in Europe, where the climate is milder and there are no such severe winters as in Russia. Therefore, there is no need to increase the temperature in the heating pipes to 70 degrees or higher. Condensation occurs most effectively when the pipes are not heated too much, when the difference in temperature between the water and the burned gas is maximum. Ideally, water at room temperature should flow through the return pipe.
Condensing-type boilers were developed in Europe, where the climate is milder and there are no such severe winters as in Russia. Therefore, there is no need to increase the temperature in the heating pipes to 70 degrees or higher. Condensation occurs most effectively when the pipes are not heated too much, when the difference in temperature between the water and the burned gas is maximum. Ideally, water at room temperature should flow through the return pipe.
Whether to install a classic boiler or a condensing boiler, which is one and a half times more expensive, is up to the owners to decide. If the house is located in the south of Russia, then gas savings will be very significant. But for northern regions with long, cold winters, the difference will be almost imperceptible - 5-10 percent.





