What is a self-tapping screw and how it happens
Modern fasteners are practical and easy to use. A striking example of this is a self-tapping screw, also known as a self-tapping screw. In most cases, the product does not even require pre-drilling.
What kind of miracle of technology is this and what types of it exist in nature - read below.

The content of the article
What is a self-tapping screw?
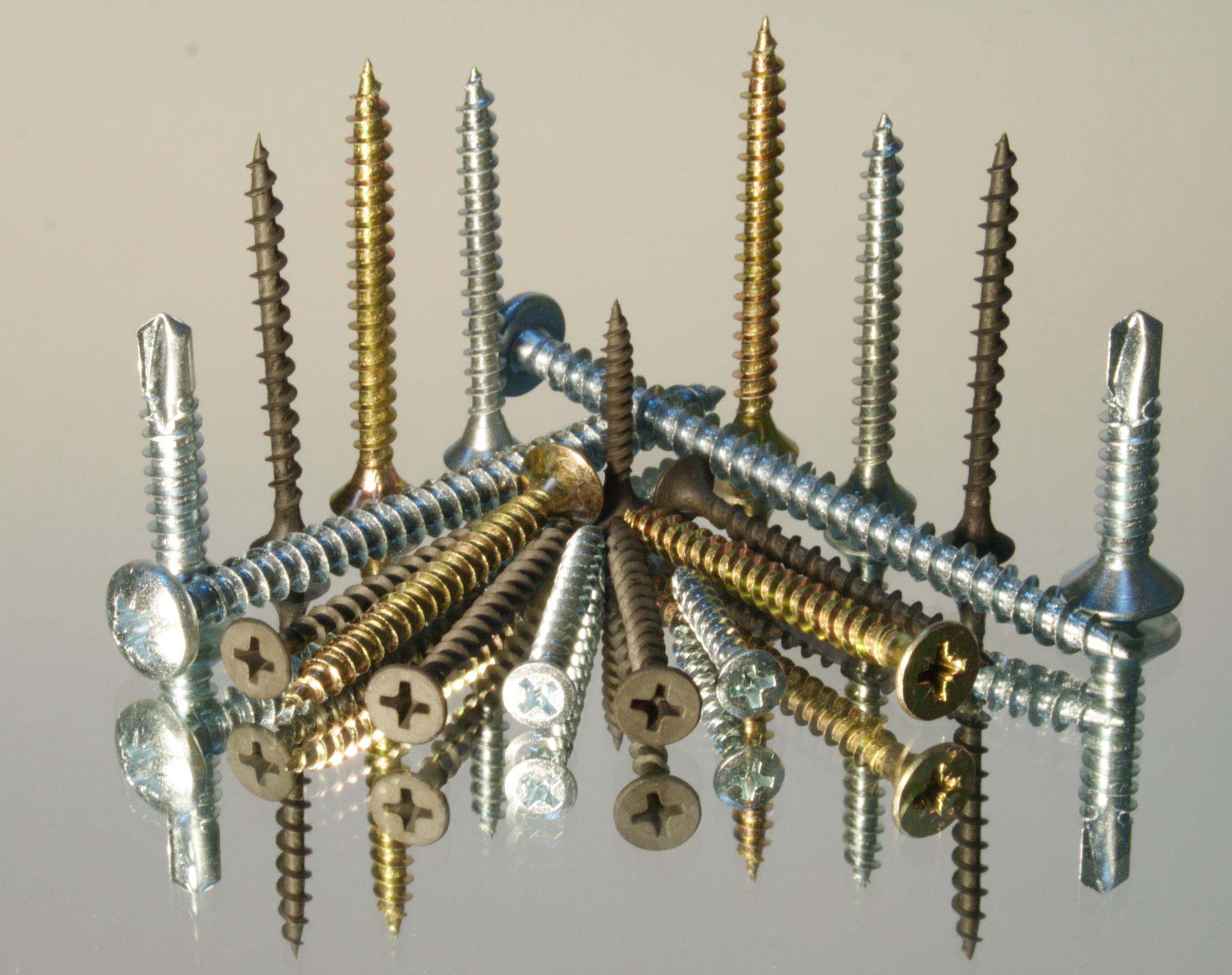
Externally, the product resembles the one known to most screw, that is, a cylindrical rod with a thread on it and a head. Thread has the shape of a triangle and serves to hold the fastener in the object being connected. The only fundamental difference with a screw is that the thread of the self-tapping screw runs along the entire length of the rod.
On the head, as a rule, there is slot under a screwdriver or screwdriver. Some varieties, for example roofing ones, do not have a slot - their head is made like a bolt and they are screwed in with a wrench of the appropriate size.
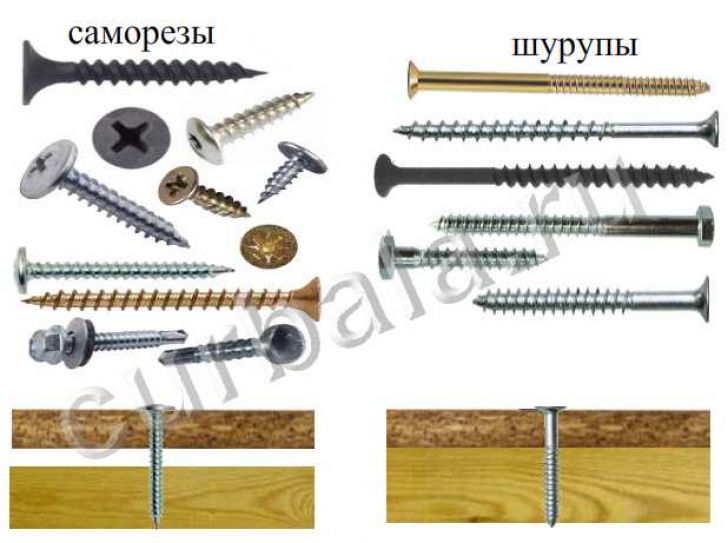
Classification of self-tapping screws
There are plenty of signs by which self-tapping screws can be divided into different groups. Let's start, perhaps, with material of manufacture:
- brass;
- stainless steel;
- made of carbon steel.
The advantage of brass is that it is less susceptible to corrosion than steel. The downside is that it is much softer, and the slot on the heads of such fasteners “licks off” with a bang. The most optimal, but also expensive option is stainless steel.

Let's go further - for protection against corrosion they use coating the following types:
- phosphating;
- oxidation;
- galvanizing
The first two types of coating are black, galvanization comes in white and yellow. There are self-tapping screws without coating, usually made of stainless steel.
By screw head design distinguish:
- secret and semi-secret;
- semicircular with and without a press washer;
- cylindrical or hexagonal shape;
- the shape of a truncated cone, affectionately referred to in common parlance as a “bug”.
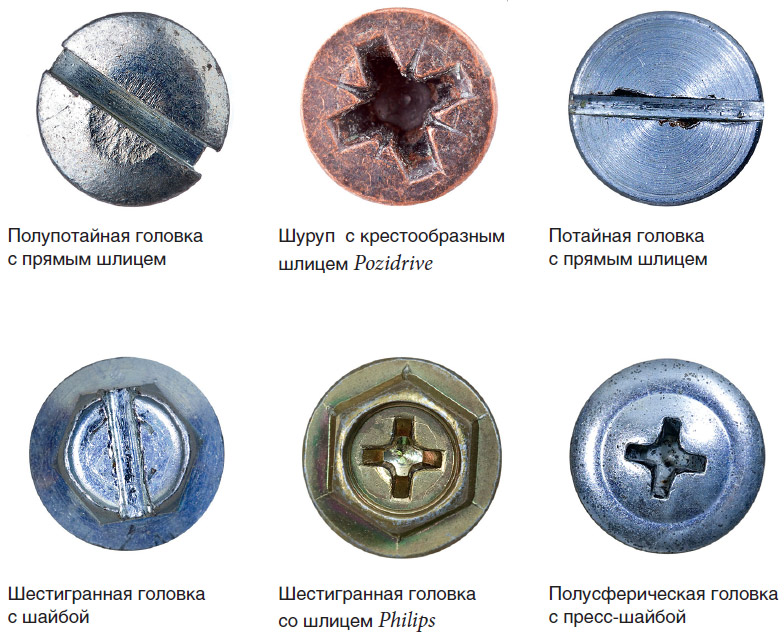

Splines There are also different ones:
- straight;
- cross-shaped standards Ph (Philips) and Pz (Pozidriv);
- hexagon shaped;
- so-called anti-vandal options in the form of various stars, triangles or other geometric shapes, requiring an exotic special key to unscrew.
The thread is classified as rare or frequent, single or double threaded. The end of the self-tapping screw can be sharp or blunt (confirmed) or made in the form of a separate drill.
Classification by purpose:
- For metal with a sharp end — made, as a rule, from carbon steel, have a frequent thread pitch. This is the most striking distinctive feature, since wood screws have much less carving. The diameter of the rod is usually 3-5 mm and varies depending on the total length of the screw. The situation is the same with the thread pitch - the longer the fastener, the thinner it is. If the thickness of the metal sheet to be fixed is less than 2 mm, then there is no need to pre-drill a hole in it. For thicker sheets, it is recommended to drill with a drill a couple of millimeters thinner than the diameter of the self-tapping screw.
- For metal with drill bit. Such products have two striking distinctive features - the shape of the head (conical or press washer) and (oddly enough) the presence of a drill.This type of self-tapping screws allows you not to use a drill at all, and the shape of the head ensures their secure fit to the surface being fixed. Metal screws are usually coated with a glossy protective shell in black, yellow or white.
- On wood - similar to self-tapping screws for metal with a sharp tip, they differ from them in a rarer thread pitch. Their coating can be either matte or glossy; the color scheme can be yellow, black or white. Their length can be up to 200 mm. The rare pitch and large thread size are due to the relatively low density and heterogeneous structure of the wood. The large thread allows you to securely hold the screw in the part. By the way, in hard types of wood, such as oak, ash, hornbeam or acacia, I strongly recommend pre-drilling, no matter what manufacturers say about their miracle products. Otherwise, the screw heads often simply cannot withstand the torque and break off. This type of fastener is widely used, in addition to wood, when working with plastic.

- Furniture confirmations - as the name suggests, they are used when assembling furniture from chipboard. Characteristic features are a blunt nose, large threads with a relatively thin head and a hexagon-shaped slot. They are screwed into a pre-prepared hole of slightly smaller diameter than the thread. This is done with a special key or a hex bit for a screwdriver. A decorative plug is usually placed on top of the confirmation head so that it does not catch the eye against the background of the laminate, which often imitates the texture of valuable wood species.
- Universal with hex head - as a rule, they are used at joints that are subject to heavy loads. Outwardly they have some resemblance to a bolt, but there are no nuts on them. They are used for fastening in wood, and in combination with a dowel - in concrete. The dowel is selected with a diameter of approximately two self-tapping screws. Tighten such fasteners with a wrench corresponding to the size of the head.
- Roofing. Distinctive features are the presence of a hex head, a rubber seal to seal the hole and a drill bit. The head is made, as a rule, with an 8 or 10 mm key, and is painted in a color corresponding to the roof. Such self-tapping screws are often supplied immediately complete with metal tiles. Their length is 19-100 mm.
Some sources cite so-called self-tapping screws for drywall, but this classification is fundamentally incorrect, since here there are fasteners for metal and gypsum plasterboard, double-threaded.





