DIY 3d scanner
 A professional scanner is very expensive and is not always a necessary thing. There is no point in buying an expensive device if you can save money by assembling a small analogue with your own hands.
A professional scanner is very expensive and is not always a necessary thing. There is no point in buying an expensive device if you can save money by assembling a small analogue with your own hands.
The content of the article
Materials and tools
To create an inexpensive version of a laser scanner, you will need the following items:
- High quality webcam.
- Line laser or any other device that produces laser beams. Remember, the thinner the beam, the better the image.
- Various fastenings.
- Data processing software.
Important points before work
It is necessary to use the device correctly so that it does not harm human health. Among the basic rules of use are:
- The laser is dangerous. It is forbidden to shine it at people and animals, especially into their eyes. There is a risk that it will cause retinal burns.
- You cannot look at the laser through optical instruments. They enhance the functions of the laser.
- It is prohibited to point the laser at household appliances and vehicles.
- Do not give the device to children.
- You should not use a laser if its power exceeds 5 mW, since even the reflection of such a beam can cause irreparable damage to health.
- Buy special safety glasses.
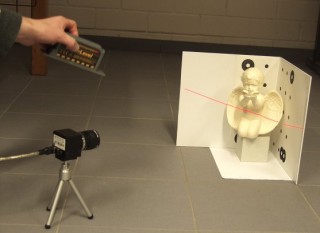
Important! If you don’t know how to use a laser, it’s better to abandon the idea of assembling a 3D scanner with your own hands.
Do-it-yourself 3D scanner: step-by-step instructions
First you need to buy a laser device.A good solution would be a module with a wavelength of 650 nm. The color is red. Power 5 mW.
Reference! If you choose a more powerful design, you will pay much more, and there is a great risk of harm to your health. It is better to opt for a self-powered laser, as it is very convenient.
If this does not work, you should find out the power parameters and create a small attachment for the battery or batteries. There will also be an on and off button. There will be two wires coming from the body kit (red and black). The first one is responsible for +, and the last one is responsible for -. It is necessary to take into account the power characteristics and polarity so that the device does not fail.
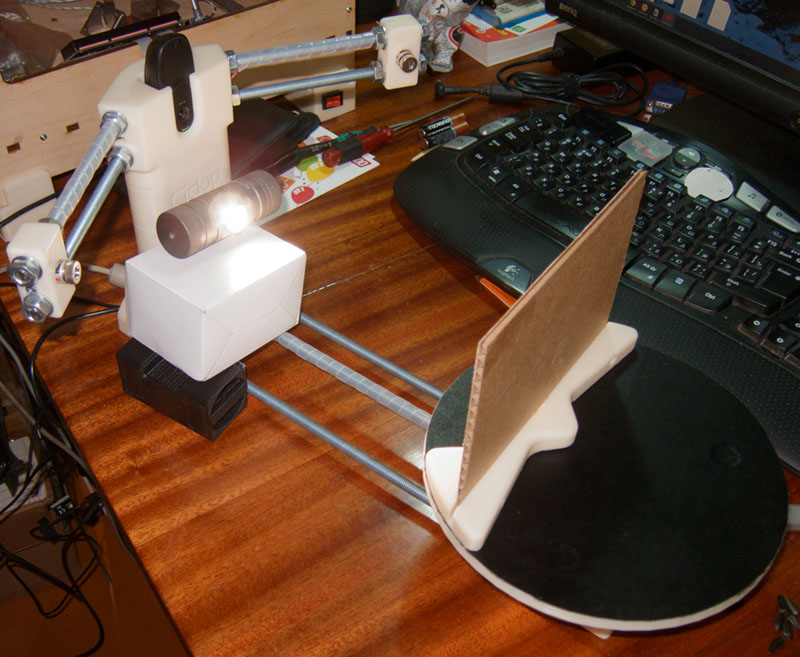

The next step is purchasing a webcam. You must select a device that supports DirectShow (it is better to choose a modern device). Most new models have required drivers.
Attention! It is also important that the webcam is capable of delivering at least 30 FPS at 640x480 resolution. You can also buy a camera whose characteristics will be slightly lower, but the quality will also decrease.
Remember, if the extension and frame rate are high, the computer will be stressed. A good choice is a Logitech Pro 9000 video camera or a Logitech HDPro Webcam 910. The best option is to choose a black and white CCD camera.
Now we need to resolve the software issue. It is necessary to convert flat images into three-dimensional models. An excellent choice is the DAVID-Laserscanner application. It has recently been updated and some bugs have been fixed. We also need Microsoft .NET Framework 2.0. But you can choose a higher version. But remember that the full version of the Laserscanner app costs more than 300 euros.
Attention! There is also a Demo version, but it is not capable of saving ready-made 3D models.
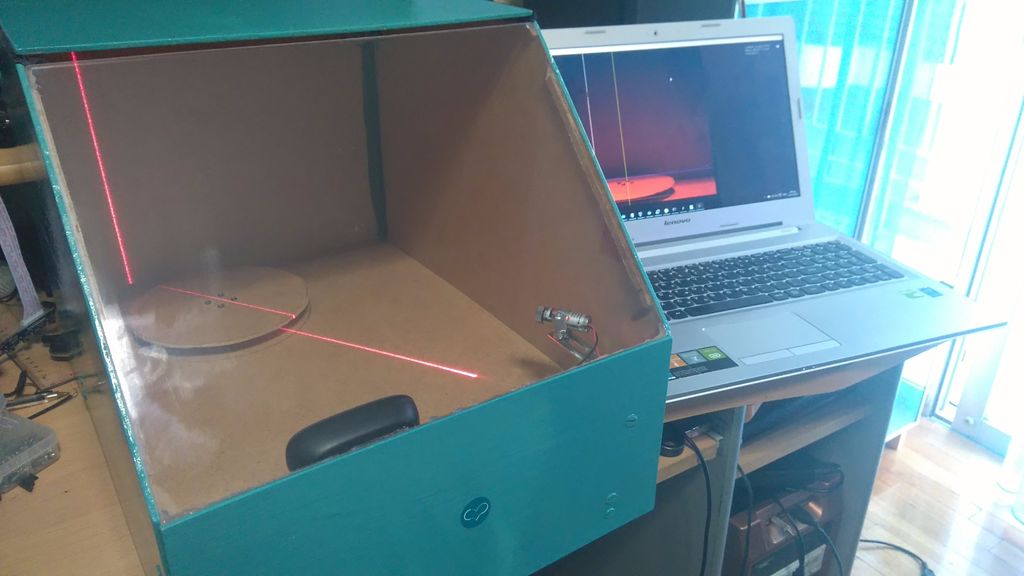
First, the program is downloaded and installed. We need to open the folder where the utility is located and go to the Printout directory. There we are looking for files for calibration for A3 and A4 formats. Formats are selected based on the size of the item to be scanned. But remember that the height of this object is approximately two times lower than the height of the calibration angle. The templates must be printed and folded along the fold line, like a book. It is important that the bend angle is 90 degrees and does not change. Also, the sheets must be even. Don't confuse the orientation. In the printouts, we measure and remember the length of the line, which is signed as a scale (Scale, measured in millimeters). We place the object that we will scan so that the created corner is behind it.
Turn on the webcam in black and white mode. She should be looking straight at the corner. We fix the device. Let's start calibration. Open the DAVID-Laserscanner program and select the camera as the source. Open the Camera Calibration section. The measured scale parameters are entered there. Click Calibrate. The program can immediately display a message indicating the success of calibration. This is good. If the message does not appear, the camera needs to be configured. We turn off everything that improves the image - autofocus, automatic brightness settings.
Reference! If you need to scan the image several times, you will have to repeat the calibration.
Now turn on the laser and point it at the sample. This is necessary to see the necessary parts of the calibration angle. You should see the laser line on both the right and left sides and on the object. Attention! Problems may arise when scanning transparent objects.They will have to be coated with paint.
Make the room dark (isolate all light sources). Again we point the laser at the sample. Ideally, only the laser line should be visible on the screen (the object and angle are not visible). Try moving the Exposure slider to increase or decrease the exposure.
Now let's start scanning. Turn on the depth display mode through Camera Shows, then Depth Map. If you move the laser down or up, the program will begin to draw the contours of the object in space. If you can’t scan the first time, you should correct the settings and just get used to the operation. For the final scan, click Stop and Erase, then Start. If you get a high-quality scan, click Stop, then Add to list. To save a copy, click Save As.
Click Stop and Erase again. The object must be constantly turned over until we stop at 360 degrees. This is necessary for the image to be three-dimensional.
Making a high-resolution scanner with your own hands is not difficult. however, it is necessary to adhere to all the rules so that the device turns out to be of high quality.





