What is IGMP snooping in a router
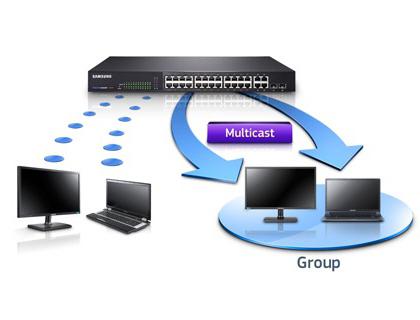 A number of platforms on the Internet use the multicast method to transmit data to a group of users. This technology is used for online games, live broadcasts, distance learning, and even mailings. But multicasting does not always correctly optimize traffic relaying and loads the user’s network, so to eliminate this problem, the IGMP snooping function was created. Let's figure out what this feature is and how to enable it to optimize your traffic.
A number of platforms on the Internet use the multicast method to transmit data to a group of users. This technology is used for online games, live broadcasts, distance learning, and even mailings. But multicasting does not always correctly optimize traffic relaying and loads the user’s network, so to eliminate this problem, the IGMP snooping function was created. Let's figure out what this feature is and how to enable it to optimize your traffic.
The content of the article
What is and why is the IGMP snooping function needed?
First, let's define IGMP to understand how the technology works. Internet Group Management Protocol is a multicast network management protocol that organizes multiple devices into groups. It is based on the IP protocol and is used everywhere on the Internet, efficiently using network resources.
IGMP snooping is the process of monitoring multicast traffic between a group of consumers and a host. When snooping is enabled, it begins to analyze user requests to connect to a multicast group and adds the port to the IGMP broadcast list. After finishing using multitraffic, the user leaves the request and protocol, and removes the port from the list of multicast data transfer.
Thus, snooping eliminates the transmission of unnecessary data to the user via multicast channels. This makes communication at the network link layer more efficient and takes into account the needs of the network layer, which is especially important for information providers. Users will also receive optimized content, although this will result in increased network load.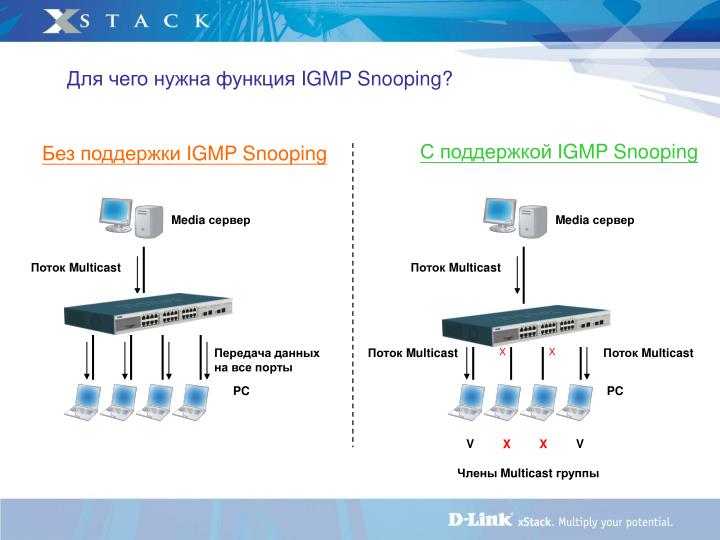
Without tracking and analyzing data, end consumers in the form of specific IP addresses will be forced to “digest” additional information that is useless to them. IGMP snooping will not only save users from unnecessary traffic, but also make information exchange more secure. Enabled tracking mode will promptly stop DDoS attack attempts on the network or specific addresses to which the Internet Group Management protocol is vulnerable.
Activating the IGMP snooping feature
The traffic tracking and analysis function is available on managed network switches or switches. This device helps implement the principles of multicast broadcasting at the network link level. To enable IGMP snooping, you must manually enable and configure it on the switch. Unmanaged counterparts do not support traffic analysis mode, since they cannot be configured through the interface.
Before using the communicator on your network, make sure that the final recipient (for example, smart-TV) supports snooping mode. Typically, devices have a corresponding item in the “Network connection setup” section, which greatly simplifies multicasting adjustments.
Let's look at how to connect the function via the command line using the example of popular D-Link switches:
- Open the device command line using the CLI interface.
- Type "enable-igmp-snooping". This command will enable the feature on the switch and all connected addresses.
- Enter "config-igmp-snooping-vlan-default-state-enable" to configure the protocol on the VLAN.
- The command “confog-multicast-vlan-filtering-mode-vlan-default-filter-unregistred-groups” enables filtering of data from several addresses at once on the communicator.
- Finally, use “config-igmp-snooping-vlan-default-fast-leave-enable” on the VLAN.
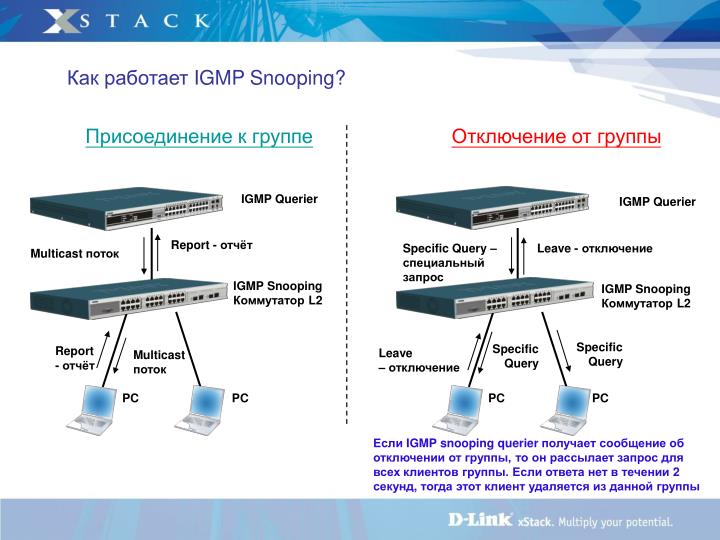
The last command enables the IGMP Snooping Fast Leave feature, which removes a port from the network as soon as the user makes a "leave" request. Thanks to Fast Leave, the consumer will not receive unnecessary data and will not process it. This will reduce the load on the network and allow the switch to operate more efficiently.
Types of IGMP snooping
Wiretapping and data analysis are divided into two types:
- Passive IGMP snooping. This protocol simply tracks data without filtering or analyzing it. In other words, wiretapping works in the background and does not in any way affect the quality of data transmission.
- Active tracking. It not only passively listens to traffic, but also filters it in order to effectively use multicasting on the network. Active IGMP snooping minimizes information exchange by filtering connection and disconnection requests to the router. The ideal state of the switch is to have one consumer for each multicast broadcast group, which is what the protocol algorithm strives for.
Snooping with an active algorithm speeds up data transfer and improves network quality, but at the same time creates additional load on the switch. Filtering requires a certain amount of memory and CPU resources from the device, while simple tracking or relaying is a less demanding procedure.At the same time, active monitoring transmits data to the router only about the most recent member of the group, so that the device does not determine this as the absence of consumers in the channel and does not exclude the port from the list.
IGMP snooping works great with home networks if you use a lot of IP multicast technologies. By purchasing and configuring a switch with the active tracking function, you will significantly speed up the Internet protocol and protect your home group from hacking and intrusion by intruders.





