How to properly apply thermal paste to a laptop processor
 The processor and video card are the most important components of a laptop. For their stable and uninterrupted operation, a cooling system is provided.
The processor and video card are the most important components of a laptop. For their stable and uninterrupted operation, a cooling system is provided.
The content of the article
Why do you need to change thermal paste?
Let's start with the definition. Thermally conductive paste is a material consisting of many components, which has high ductility and thermal conductivity. Its usual composition is silicone combined with zinc oxide. There may be inclusions of silver, ceramics and carbon, which increase efficiency.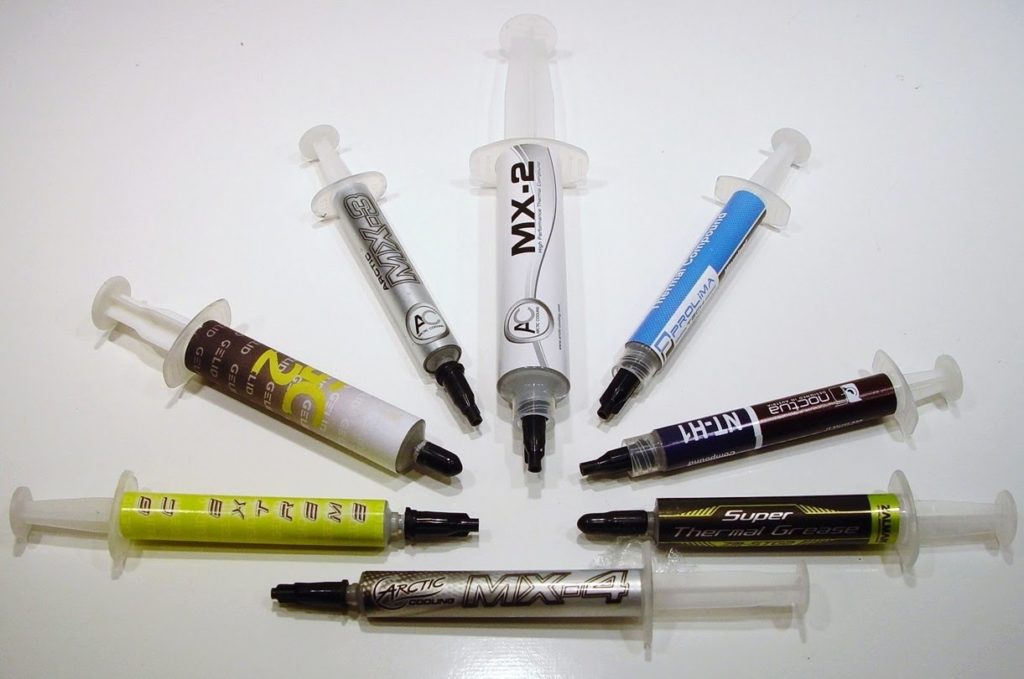
The purpose of the application is to increase the contact area between laptop elements. This substance fills microscopic irregularities (cracks, depressions) of the processor and radiator. The result is improved heat transfer from the computer device to the cooling devices.
In the absence of paste, air gaps may form, preventing heat transfer. The stability of the chip decreases and it begins to overheat. Sudden computer reboots occur, which temporarily reduces the processor temperature.
How often should you change thermal paste?
Over time, the thermal paste begins to dry out and gradually loses its thermal conductivity properties. The plastic layer turns into powder or hardens.
The wear period may vary depending on the following conditions:
- grade of material;
- operating surface temperature;
- chip load level.
If a high-quality layer has been applied, operating in a stable temperature environment and under moderate loads, the period of its use can reach 5 years or more.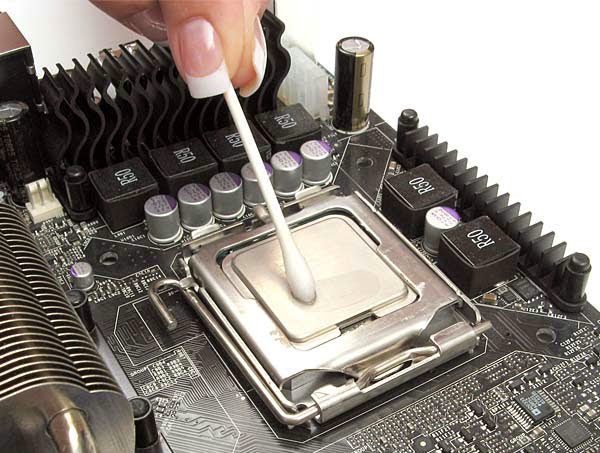
Cheap analogues wear out much faster and may need to be replaced within a year.
Normal CPU temperatures:
- operating mode up to 65 degrees;
- in idle up to 45 degrees.
The user can find out about the chip overheating either by external signs (crashes, sudden system reboots) or by going into Bios (using the F8 key or others prescribed for your PC). However, the menu options do not indicate load temperatures.
Reference! There are special programs for Windows that determine the degree of processor heating. Among the free products are Core Temp, CPUID, Speccy, etc. The applications have a user-friendly interface and ease of use.
How to choose thermal paste for a processor
There are several varieties of material used depending on the specific component of the laptop that needs to be cooled.
Liquid metal is a liquid mass or gasket.
Advantages: high thermal conductivity, possibility of application at sub-zero temperatures.
Disadvantages: high price, aggressive components, conductivity. Do not use on aluminum surfaces, processor covers or other sensitive elements.
Thermal pads, a universal material used on components without increased requirements.
Pros: elasticity, fills voids of any shape and size, maintaining stable thermal conductivity.
Cons: Does not provide adequate cooling for the CPU and GPU.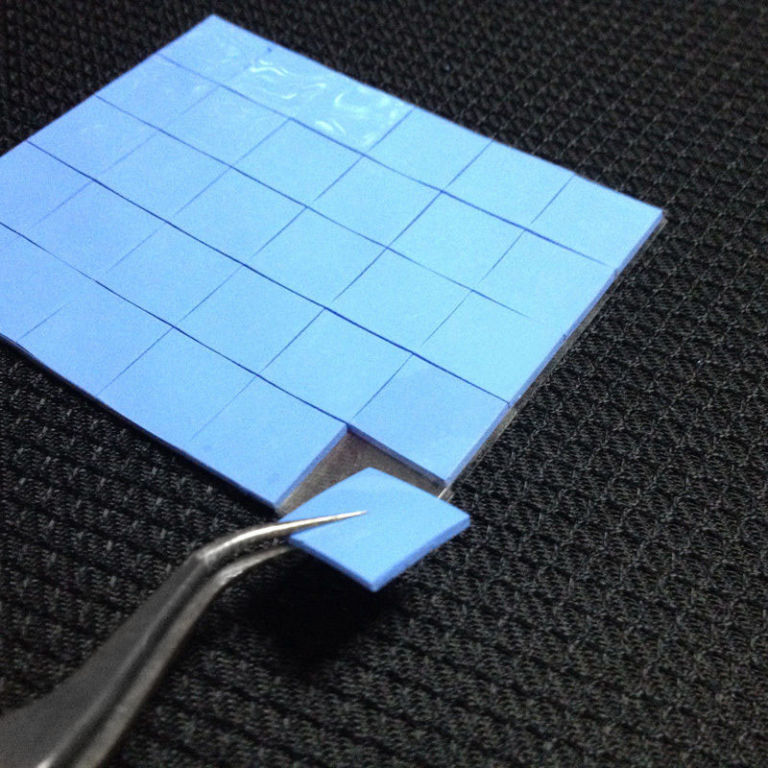
Hot-melt adhesive, after application, forms a high-strength connection.
Advantages: fixes parts in places where appropriate fasteners are not provided.
Disadvantages: low thermal conductivity.
Standard thermal paste is a commonly used compound with high heat transfer properties.
Advantages: the result is higher than using thermal pads and hot glue, suitable for any surface.
A type of paste with additions of copper and gold will provide cooling for the most powerful processors.
Disadvantages: Requires minimal space between the chip and the cooling system.
Important! The main parameter of the layer is heat conductivity, but it does not always reflect the effectiveness of application. The composition should be selected based on professional responses in authoritative media, since they are formed on the basis of well-conducted tests with reliable results.
The most popular brands with positive reviews from both experts and users:
- KPT-8;
- AlSil3;
- AlSil5.
These are domestically produced products. Their characteristics: high thermal transfer, durability of the applied layer, affordable price.
Among the imported options we can note:
- TITAN;
- ZALMAN.
These materials showed high-quality test results.
Reference! Pastes are available in various packages: syringes, tubes, bags. Syringes are the most convenient: they allow you to easily dose and apply the material.
How to apply thermal paste correctly
Preliminary actions will require removing the old layer of the substance. To do this, carefully remove the radiator and cooler from the processor.
The paste can be in the form of a plastic substance, in which case we remove it using an alcohol solution, moistening a cloth (cotton swabs, sticks, etc.) in it.
The material applied long ago loses its properties and dries out, sticking to the surface. It will require painstaking cleaning.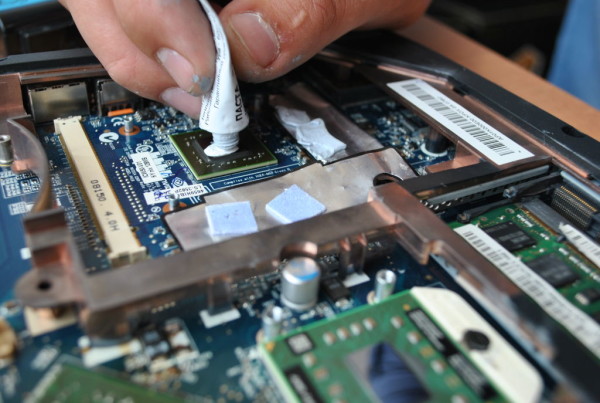
Important! When processing, avoid damaging computer parts; even a minor scratch can distort temperature conditions and impair the performance of components.
An effective but time-consuming method is an eraser. It is necessary to clean the surfaces of particles until they shine. To make the task easier, the radiator can be treated with other objects (wooden slats, etc., but without sharp objects).
Attention! When using a rubber band on the processor, the component remains in the motherboard socket to avoid damage.
Let's move on to applying a new layer. We follow the rules:
- The material is taken in a minimal amount (about the size of a match head), less for a video card chip (no more than 1 gram).
- Apply evenly over the entire surface, maintaining the same thickness of the paste.
- We process it so that the material is laid down in as thin a layer as possible.

No gaps are allowed; the coating must be continuous.
Following the recommendations will ensure maximum contact surface and a high degree of cooling.
Attention! One-time PC prevention will require one thermal pad and up to 2 grams of thermal paste.
We talked in detail about the features of heat-conducting paste, its scope of application and application methods.
As we read, we learn that thermal paste has high thermal conductivity, henceforth it is called an insulator! About KPT-8 and AlSil it is said “Their characteristics: high thermal insulation”! The article is about laptops, but the images do not show the insides of laptops! It's a shame, gentlemen!
Hello! Thanks for the note, the article has been corrected

not an article, but Tina didn’t tell me how and with what to apply a uniform thin layer, just splashed water and the usefulness was 0, then other headings should be put






I remembered: “Smeared - l*x.” If I didn’t smear it, I’m still a l*ck.”
In fact, you can smear it, or you can simply squeeze out a drop, after which the radiator base will distribute the paste evenly and over a sufficient area. Perhaps the only argument in favor of “be sure to smear” is a lack of experience or a poor eye. If you're not used to it, you can squeeze out so much that the paste comes out like the sides of Baba Zina.