How do headphones work?
 Since the appearance of the first headphones, their design has not changed fundamentally. Only the sound quality has improved, the capabilities have expanded and the appearance has changed - the accessory has become more compact. Today, an assortment of all kinds of headphones and headsets allows you to choose a model in accordance with individual needs. What is this accessory?
Since the appearance of the first headphones, their design has not changed fundamentally. Only the sound quality has improved, the capabilities have expanded and the appearance has changed - the accessory has become more compact. Today, an assortment of all kinds of headphones and headsets allows you to choose a model in accordance with individual needs. What is this accessory?
The content of the article
The design of headphones, their main components
There are two main types of headphone designs:
- with headband - overhead, monitor;

- without a headband - in-canal or “droplets”.

In addition, the accessory is divided according to the degree of closure.
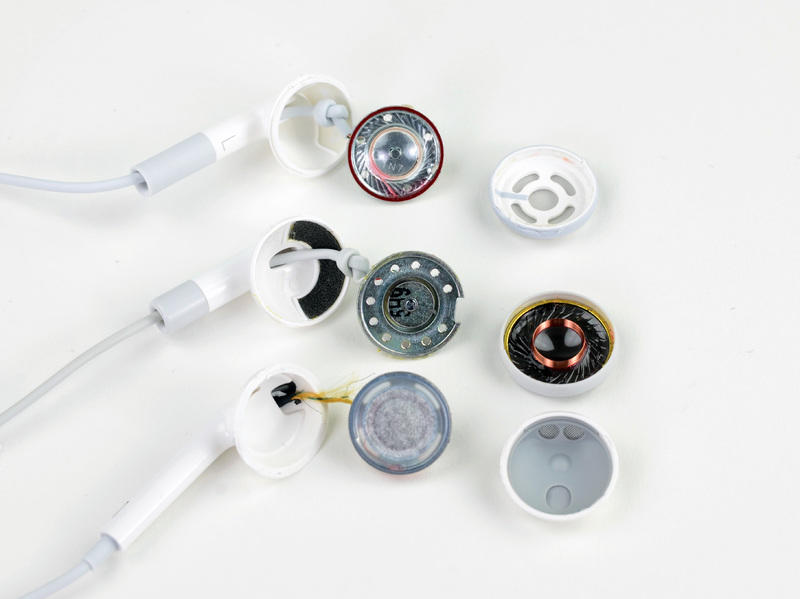
Regardless of the type, the headphones are designed almost identically and consist of the following components:
- Plug. It is an adapter between the playback device and the speakers.
- The wire. Designed to transmit electrical vibrations to speakers.
- Speakers. Built into the body. Receiving a signal, they create acoustic vibrations and transmit sound to the ear.

REFERENCE! There are also wireless models. The signal is supplied to them via available radio frequencies. The closer the signal source, the better its quality.
Principle of operation
The specific operation of the acoustic device is simple. A magnet attached to the body creates a magnetic static field, within the range of which the coil is placed. It is supplied with alternating current from the playback device.
The difference between alternating and static voltage contributes to the movement of the coil, which is transmitted to the membrane. The latter, in turn, repeats the movements of the coil. These vibrations are perceived as sound.
REFERENCE! The principle of reproduction in full-size accessories and in so-called droplets is somewhat different. The latter have an armature on the coil, which perceives its vibrations and transmits them to the membrane through a rigid connection.
Modern good quality headphones are capable of transmitting sound over a wide range of frequencies - from 5 to 25,000 Hz.