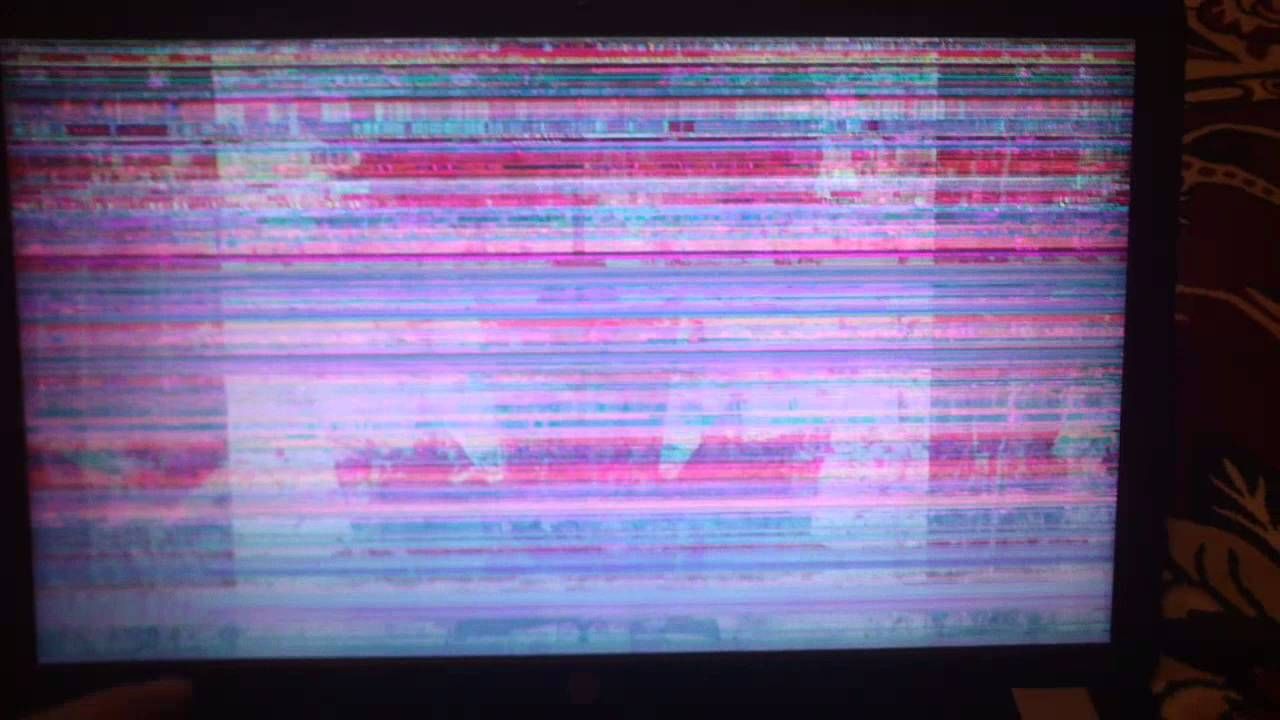
I changed the processor and the monitor does not turn on
 When searching for RAM, you may see mention of its compatibility with AMD or Intel processors. Don't worry, this doesn't mean one won't work for the other.
When searching for RAM, you may see mention of its compatibility with AMD or Intel processors. Don't worry, this doesn't mean one won't work for the other.
The content of the article
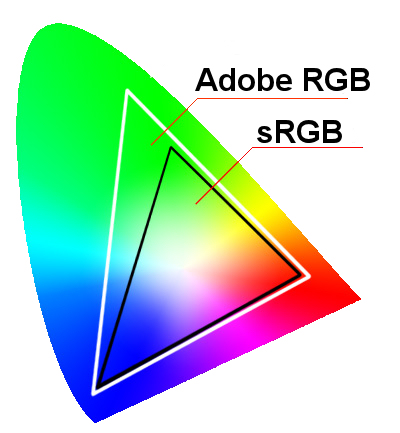
How to check if your monitor and processor are compatible
Often RAM comes with two manufacturer-set "XMP" profiles that are optimized for a specific microprocessor. Most microprocessors of any brand typically operate with these profiles, although sometimes a little tweaking may be required for higher rated speeds.
To make sure your motherboard will be compatible, you'll need to look at what socket and chipset your microprocessor is compatible with. Such a check is needed, for example, when, after changing the monitor or processor, the monitor does not turn on.
A socket refers to the physical connector on the motherboard that holds your microprocessor in place. This can be easily determined by simply looking at the socket size for the processor and motherboard you are going to use.
REFERENCE! If you try to connect a microprocessor to the wrong socket type, you may damage the processor and/or motherboard. Then you can’t do without replacement and additional costs.
How to check the connection

The first step to figuring out if your PC's processor is running is to see what happens immediately after you turn it on. This is because many motherboards produce different beeps to indicate problems. Another way is to connect the processor to a test computer that has working hardware and is compatible with the microprocessor you want to test. You should only work on your PC's internal hardware if you have enough experience in computer repair to avoid further damage to it.
- Unplug the power cord from both computers (on the laptop, also remove the battery). Remove the heatsink and microprocessor from the computer that you suspect has a faulty electronics unit; Also remove the microprocessor and heatsink from the test computer if you have not already done so.
- Connect the microprocessor and heatsink to a second test computer that uses the same type of processor. Connect the power cord.
- Turn on your computer. If your PC won't boot into the BIOS or produces the same beeping pattern, it's likely that the processor isn't working.
What other reasons are there?
 Consider the fact that even if you think your electronics unit is damaged, it most likely is not.
Consider the fact that even if you think your electronics unit is damaged, it most likely is not.
REFERENCE! More often than not, the symptoms you think indicate damage are due to problems unrelated to your electronics unit.
Before you take steps to diagnose problems, consider whether the two main causes of damage have occurred in the recent past—electrical problems, such as a power surge or device malfunction, or liquid in the computer.Next, remove the case cover to expose the insides of your computer, get your user manual, and start figuring out if your processor is actually damaged.