What are the monitor screen resolutions?
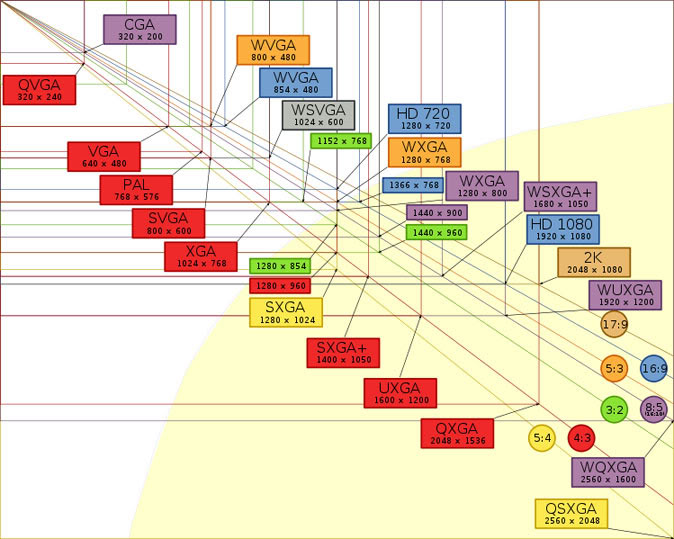 If you've been following along so far, you've most likely already come to the conclusion that, in terms of screen resolution, bigger is better. Well, that's not necessarily the case.
If you've been following along so far, you've most likely already come to the conclusion that, in terms of screen resolution, bigger is better. Well, that's not necessarily the case.
When using two screens of the same size, the higher resolution screen will display more content and result in less scrolling. In addition, the image will be clearer.
However, the trade-off is that the image will also be smaller. This strains your eyes and in extreme cases you may need to zoom in to see it properly. Since you'll be enlarging the picture, less of it will fit on the display, you're essentially using a smaller one. So what's the point of purchasing a device with a higher resolution when you won't be able to use it effectively?
The content of the article
What monitor resolutions are there?
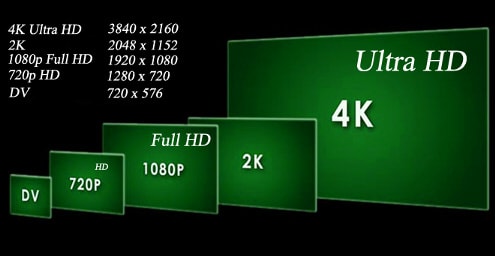 720p = 1280 x 720 - often called HD, “HD Ready”
720p = 1280 x 720 - often called HD, “HD Ready”- 1080p = 1920 x 1080 - often called FullHD
- 2K = 2048 x 1080 - This refers to displays with a horizontal resolution of around 2000 pixels. Although it is close to 1080p, it is considered the standard.
- 1440p = 2560 x 1440 is common and is called QHD or Quad HD and is mainly found in gaming monitors and high-end phones. 1440p is 4 times the resolution of 720p HD or “HD ready”.
- 4K or 2160p = 3840 x 2160 is also widely used and is called 4K, UHD or Ultra HD.Is huge for a standard screen, and is found in premium screens and computer monitors.
REFERENCE! 2160p is designated 4K due to the width being close to 4000 pixels. In other words, it produces 4 times more pixels than 1080p FHD or "Full HD".
- 8K or 4320p = 7680 x 4320 – referred to as 8K, it produces sixteen times more pixels than standard 1080p FHD or “Full HD”. For now, 8K is only available on expensive TVs from Samsung and LG. You can check if your computer can display such a large amount of data using an 8K video example.
What determines the choice of resolution?
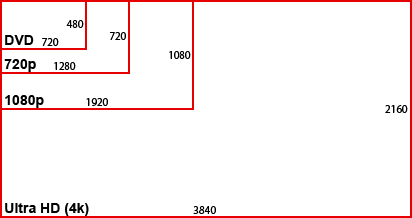 You might think that even if you don't desperately need high resolution since it's available, why not get it. There are several reasons.
You might think that even if you don't desperately need high resolution since it's available, why not get it. There are several reasons.
The first is money. Still, a screen with a high dot content costs more.
The second reason is technical. Still, higher resolution requires more resources.
If you set the screen refresh rate to sixty hertz, your video card refreshes the frame sixty times per second. For most people, a frequency of sixty hertz is low, and if possible they will operate at a frequency of one hundred twenty hertz or one hundred forty-four hertz. The greater the number of points, the higher the load on the video card.





