Who invented the battery
It is impossible to imagine our life today without electricity, and in this case we are talking not only about the current coming “from the network”, but also about batteries that can store energy within themselves for a long time. These include a regular “finger-type” battery, which can be found in a wall clock, TV remote control or wireless laptop mouse. But who is the author-inventor of this most useful device, and what do experiments on frogs have to do with it?
The content of the article
Italian experiences
First, let's move back to the end of the 17th century, when an Italian scientist named Luigi Galvani conducted his numerous experiments devoted to the study of the reaction of living tissue to electricity. Galvani was a physician by profession, and the specifics of these reactions were of great interest to his field of study.
As experimental subjects, the scientist used ordinary frogs, to which, no matter how cruel it may sound (in the 17th century there were not many animal protection organizations), he connected a pair of electrodes. At the same time, the scientist made a slight mistake in his interpretation of the process discovered in this way, and although much later his discovery was “brought to fruition” by other scientists, the fame of the inventor was assigned to him. The very name “galvanic cell” refers to the name of the famous Italian.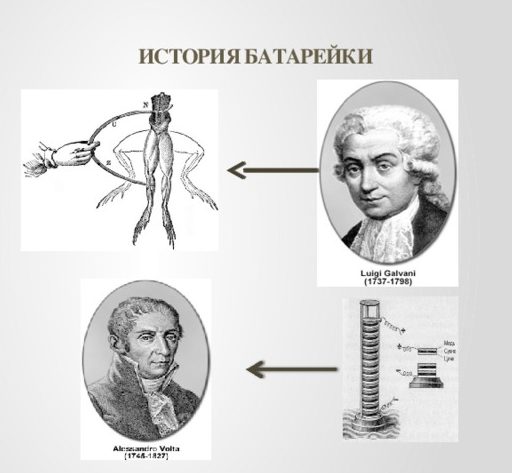
Reference. Based on the results of Galvani's work, the talented Italian physiologist, chemist and physicist Alessandro Volta was able to prove that in order for current to pass between two electrodes, it is necessary to place them in a suitable environment. As such a medium, the physicist no longer took the paw of an unfortunate frog, but a saline solution. Thus, the world's first autonomous power source was created. However, it very, very vaguely resembled an ordinary “finger-type” battery.
Principle of operation
For a deeper understanding of the topic, you should have a general understanding of how such batteries generally work. So, a typical battery consists of two electrodes (cathode and anode) and an electrolyte between them. Electrodes under the influence of electrolyte are exposed to acid-reduction reactions, which leads to the flow of electric current between them.
First battery
The scientific community has long worked according to one principle: in fact, each subsequent study is carried out on the basis of the previous one, and each new invention is carried out on the basis of the previous one. This axiom was followed by the French physicist Gaston Plante, who in the 19th century, based on Volta's research data, made a new successful experiment by creating a battery that recharges from third-party power sources.
The basis for the new invention was two lead plates, a special container and sulfuric acid. Today every car enthusiast can see the “results” of such successful inventive activity under the hood of his car: most batteries in modern cars work on approximately the same principle as the invention of more than a century ago.
A battery for everyone!
Previously, we looked at batteries in which the electrolyte was liquid, but many who, despite the prohibitions of adults, disassembled batteries in childhood, remember that there is no liquid inside them. The first dry cell battery was invented, in fact, by several scientists, but the first of them was a man named Georges Leclanché.
This scientist conducted an important study in 1868, which was continued in his time by the German Karl Gassner. Based on the data obtained from these two studies, another German scientist, Paul Schmidt, designed the first dry battery.
Reference. In addition, Paul Schmidt is known throughout the world as the inventor of the flashlight.
The further history of the development of the “battery” industry moves away from individual bright minds and moves into the sphere of industry. The first battery to be mass produced went on sale in 1992 in the USA. The Eveready Battery Company, a little-known company at that time, today supplies batteries under the Energizer brand to most countries of the world.
The first "pills"

Batteries with a round, flattened shape, popularly called “tablet” batteries, were first invented back in the 40s of the 20th century. Initially, they were used exclusively by the American military and were designed specifically to withstand temperature changes and mechanical damage.
This “tablet” contained zinc and mercury, which increased the power available to it and its performance. By the way, these batteries were invented by Samuel Ruben, one of the future founders of Duracell.





