What is a battery?
The word “battery” has now come to mean a fairly wide range of different power sources. It is used very often, but not everyone knows what it is, what types there are, when and who invented it. Even such a simple example - in French, English, Russian, and many other languages, this word is written almost identically. What does it originally mean, this word? Today’s article will briefly tell you what a battery is – the meaning of the word itself, the device, and the history of its invention.

The content of the article
Origin of the word
We owe the appearance of the word itself to the development of military affairs, in particular firearms. In general, it is correct to use the word “battery” to describe two or more galvanic cells connected in a circuit in parallel or in series. Today they call one element this way, without thinking about the fact that this is incorrect from a logical point of view.
The word itself is of French origin, derived from "battre", that is - "beat". The term originally referred to artillery, then came to mean any combination of similar elements to work together.

When were galvanic cells discovered?
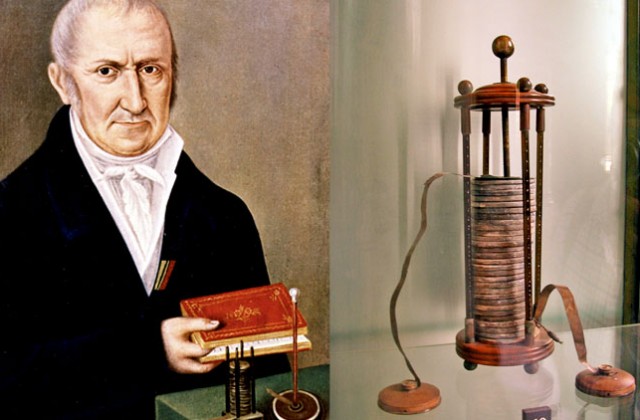
If we do not take into account the statements of archaeologists that even in Mesopotamia around the 1st century BC.there was a working prototype - the so-called Baghdad battery - then the first work in this area belongs to Luigi Galvani, Italian, and date from the end XVIII century. There is no direct evidence for this statement - it is just a hypothesis.
The first battery of galvanic (the name seems to hint at where the legs grow from) elements was assembled Alessandro Volta V 1798 year. It consisted of disks connected in series from an alloy of copper and zinc, separated by cardboard soaked in saline solution. The invention was called "volt pole".

To whom do we owe the massive use of miniature batteries?
The credit goes to the founder of the company Eveready (in plain language the name translates as “always ready”) Conrad Hubert. Back in 1898, he invented an electric flashlight, powered by a D-size dry cell battery.
A technological breakthrough was made by the same company Eveready in the late 50s of the last century, when cylindrical batteries similar to modern ones were introduced into use.

And we owe the appearance of lithium batteries to the company Energizer, which released the first prototype size AA in 1992. In addition, the company has invested a lot of effort and money to ensure that manufacturers stop using mercury in the manufacture of power supplies.
This is interesting. Today, batteries of sizes AA, AAA, AAAA, C and D are produced at the same voltage - 1.5 volts.
Principle of operation
Despite the different compositions used in the production of batteries today, they all work on the same principle. Any of them has two poles - positive (anode) and negative (cathode), the space between which is filled with electrolyte in a liquid or solid state. The current is directed from the anode to the cathode, and between the poles there must be a load - a light bulb, a motor, a control panel, and so on. If the poles are connected without load, there will be short circuit with intense heat release.
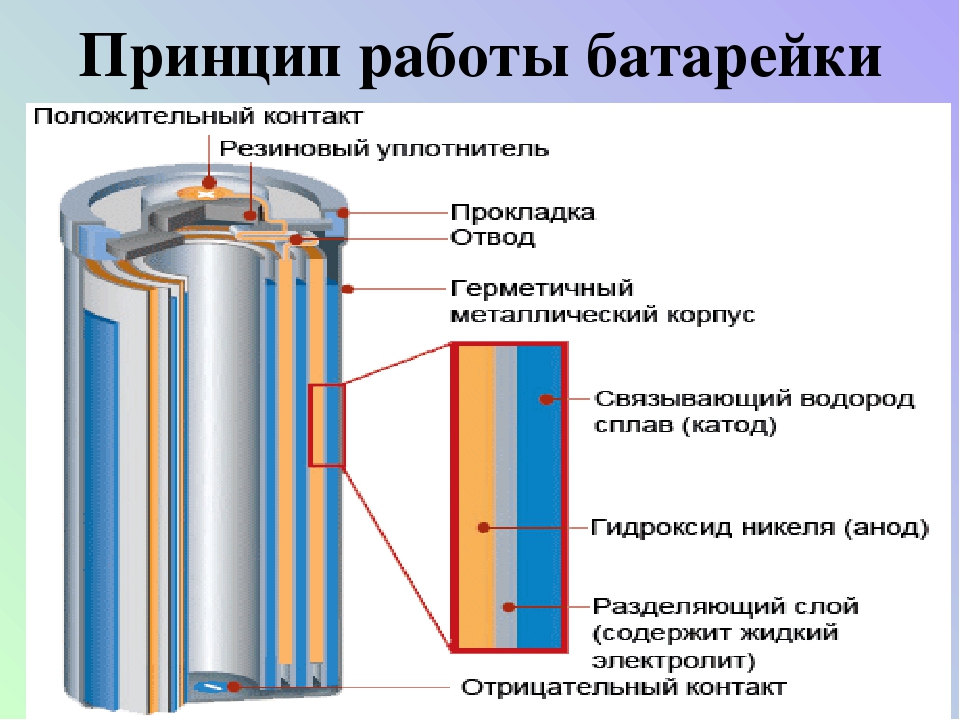
Reversibility of chemical reactions
What is noteworthy: during the operation of the battery, its chemical composition changes, and it, as they say, runs out. In some cases, this process is irreversible, so there is nothing left to do but simply throw away your used power source. But the process of making rechargeable batteries is getting cheaper, and the resources on Earth are not endless. Therefore, disposable batteries are gradually going out of fashion. In addition, they must be disposed of in a special way, otherwise serious environmental pollution will occur.

Lithium-ion batteries
Modern lithium ion batteries, used in cars, cell phones and many other products, meet the requirements for repeated charging, up to several thousand cycles, without much loss of operating time.





