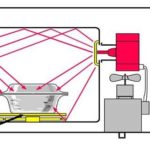
Operating principle of a waste oil furnace
 An example of structures whose operation reduces the negative impact on the environment is a heating furnace, where any waste oil, from transmission oil to vegetable oil, is used as fuel. Therefore, there are no problems with fuel for such structures. In addition, there is no need to purchase expensive materials for the manufacture of the heating unit itself. For these purposes, a used propane or oxygen cylinder or scraps of construction metal will be suitable.
An example of structures whose operation reduces the negative impact on the environment is a heating furnace, where any waste oil, from transmission oil to vegetable oil, is used as fuel. Therefore, there are no problems with fuel for such structures. In addition, there is no need to purchase expensive materials for the manufacture of the heating unit itself. For these purposes, a used propane or oxygen cylinder or scraps of construction metal will be suitable.
The content of the article
Operating principle of a waste oil furnace
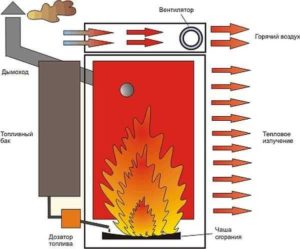 This unit operates on the basis of pyrolysis, when decomposition and gasification occur when burning organic fuel. Initially, when heated, complex nitrogen-carbon chains of oil molecules split into chemical elements, after which, under the influence of oxygen, they are oxidized and then cooled, turning into safe nitrogen and water vapor as they go.
This unit operates on the basis of pyrolysis, when decomposition and gasification occur when burning organic fuel. Initially, when heated, complex nitrogen-carbon chains of oil molecules split into chemical elements, after which, under the influence of oxygen, they are oxidized and then cooled, turning into safe nitrogen and water vapor as they go.
If the stove is designed correctly, all dimensions and shape are observed, then the fuel will burn with the greatest efficiency, and carbon particles in the form of soot and soot will not settle in the chimney.
In such a heating device there are three zones:
- in the first, the vapors of oil heated to boiling occur;
- in the second - gasification of waste;
- the third is a chamber for afterburning flammable substances and reducing the temperature jump.
In the lower chamber there is a reservoir with waste oil. When organic fuel boils, the stove goes into operating mode. The resulting steam ignites. Turbulent flows arising in the first zone act as a limiter and, due to this, the burning mixture does not have free access to the pyrolysis zone. This is how self-regulation occurs. In addition, under the influence of inertial force, burning gases swirl into a vortex flow.
The air required for exhaust combustion is supplied through a window with a damper, which controls the rate of oil combustion and the power of the heating unit. If the damper is closed completely, the stove will go out.
The oil vapors twisted into a spiral bundle enter the high-temperature afterburning chamber. Essentially, it is a pipe of a certain diameter and length, with many holes for air. Here, gases are mixed with oxygen, and the oxidation process takes place quite intensively. Temperatures in this zone can reach 900 °C or higher, causing nitrogen to become more reactive. Nitrogen and carbon oxides collect at the top of the pyrolysis zone.
Complete combustion of unburned gasification products occurs in the upper chamber of the furnace. Its design features are such that they make it possible to reduce the temperature jump. Nitrogen, which loses activity at low temperatures, is again replaced by oxygen. Thus, at the output we obtain safe nitrogen in a gaseous state, heated water vapor. Solid carbon monoxide is released through the chimney.
Advantages and disadvantages of mining furnaces
Simplicity of design, low fuel consumption, ease of operation - these are the factors that make these heating units especially attractive. In addition to this, they have a number of other advantages:
- Effectively and quickly heat enclosed spaces.
- Does not depend on the availability of electricity or gas.

- You can use the oven for cooking.
- The dimensions and weight of the structure allow it to be transported if necessary.
- No open fire.
- The furnace allows you to burn waste oil and its vapors, and, subject to operating conditions, is not a fire hazard.
Despite the large number of advantages, this design has many disadvantages:
- The need to filter the oil, otherwise the impurities present in it may clog the supply tube.
- A chimney that is too high to create draft is required, more than 4 m high.
- High temperature of equipment surfaces.
- The chimney and stove have to be cleaned daily.
- Dirt in the room, noise during operation and an unpleasant odor.
- Possibility of fire if the combustion chamber is overfilled with waste.
- The heating unit goes out only when the fuel is completely burned.
IMPORTANT! You can start cleaning the oven only after it has completely cooled down.
Application area
Waste oil furnaces also have other names: heat guns, air heaters. They are used extremely rarely for heating residential premises, since due to the presence of hot surfaces the air dries out. But they are ideal for industrial premises because they heat the air very quickly.
They are usually used for heating greenhouses and garages, service stations and car washes, etc. Modified designs with a coil can be included in a water heating system.