Types of water circulation in a steam or gas boiler: diagram, frequency
Water circulation in the boiler is a key process that ensures efficient and safe operation of equipment. Water, when heated in a boiler, turns into steam, which is then used for heating or in industrial processes. The efficiency of water circulation directly affects the boiler's performance, energy efficiency and service life.
The content of the article
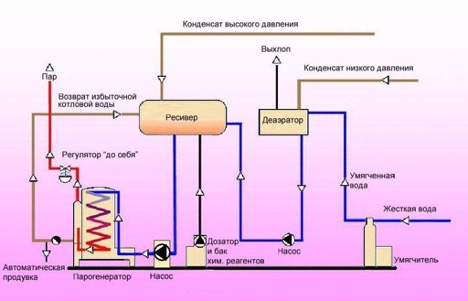
Types of water circulation in boilers
Water circulation in heating systems plays an important role in ensuring the efficient operation of heating equipment. Depending on the design and operating principle of the boiler, various types of water circulation in boilers are used. Each of these types has its own characteristics. They determine the choice of a specific type of circulation for specific conditions and requirements.
Perhaps the most common type is the natural circulation of water in the boiler. This process is based on natural physical laws. Heated water, which has a lower density, rises. And the cooled, denser one goes down. Thus, a natural circulation circuit is formed, which ensures constant movement of water in the system. This circulation method is easy to implement and does not require additional equipment such as circulation pumps.
However, as the size and power of the boiler increases, natural circulation may become ineffective.In such cases, forced circulation is used, which involves the use of pumps to move water through the system. This method allows you to control the speed of water movement, which is especially important in large and complex heating systems, as well as when there are high requirements for temperature and water pressure.
Main types of circulation:
- Natural circulation is typical for small and medium-sized boilers and is easy to implement.
- Forced circulation is used in large and high-performance boilers and requires the installation of circulation pumps.
- Combined circulation combines elements of natural and forced circulation and is used in boilers operating in various modes.
The choice of circulation type depends on many factors, including boiler power, its design, operating conditions and heating system efficiency requirements. A competent choice of circulation method ensures optimal boiler operation, energy savings and durability of the entire heating system.
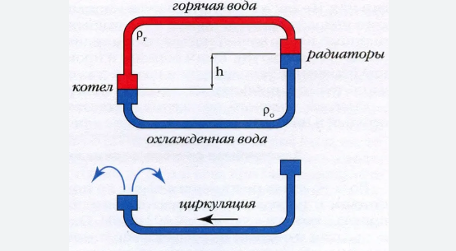
Circulation scheme and frequency
The circulation pattern in the boiler determines the path along which water moves within the heating system. This is a key element that determines the efficiency and reliability of the boiler. The water circulation pattern in the boiler may vary depending on the type of boiler and its operating principle. For example, in steam boilers with natural circulation, water moves through vertical pipes, heats up, turns into steam, which rises, cools and falls down again, forming a closed cycle.
The circulation rate is a parameter showing how many times water passes through the boiler over a certain period of time.This parameter is important to maintain the efficiency of the boiler and prevent it from overheating or underheating. The circulation ratio of a steam boiler determines the frequency with which water is converted into steam and back. The water circulation in a gas boiler usually has a higher ratio due to the more efficient combustion process and heat transfer.
The main factors influencing the circulation pattern and frequency:
- Type of boiler - it will be steam or hot water, natural or forced circulation.
- The power of the boiler determines the volume of water that needs to be heated and pumped.
- The design of the boiler and the location of the pipes affect the path of water movement.
- Energy efficiency and performance requirements. High circulation rates can improve efficiency but require a larger pump system.
The correct choice of circuit and determination of the circulation frequency allow optimizing the operation of the boiler, ensuring its high efficiency and reliability. This also helps reduce energy consumption and extend the life of your heating equipment.
Conclusion
Proper water circulation is the key to efficient and safe operation of various types of boilers. Whether it is a steam or gas boiler, it is important to take into account the features of water circulation, choosing a suitable scheme and calculating the required circulation rate. This approach ensures maximum equipment efficiency and longevity.





