Learning to figure out which pump is better: vortex or centrifugal
For private water supply, two types of pumps are most often used - vortex and centrifugal. Such devices are installed in domestic premises to drive water through pipes and lift it from the bottom of the well, and sometimes they are also found in industrial premises.
Now we will figure out which pump is better - vortex or centrifugal, design features of centrifugal and vortex pumps, the operating principle of a centrifugal pump, how a vortex pump works, advantages and disadvantages of centrifugal/vortex pumps. At the end of the article you will find a table with the criteria for choosing a pump.
Features of centrifugal and vortex pumps. Types of pumps. How centrifugal/vortex pumps work. What is the difference between a centrifugal pump and a vortex pump?
The operating principle of all pumps is the same - liquid/gas enters on one side, and is pushed out from the other, receiving kinetic energy from the pump mechanism.
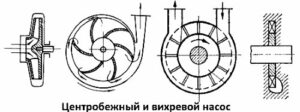
Pump mechanisms may be different. Based on them and the type of energy transfer from the mechanism, the following types of pumps are distinguished:
- Water lifting wheel
- Archimedes screw
- Piston
- Winged
- Vane rotor
- External gears
- Internal gears
- Cams with sickle-shaped rotors
- Impeller
- Sinus
- Screw
- Peristaltic
- Vortex
- Centrifugal
- And others
In centrifugal pumps, liquid/gas is pumped directly into the center of a wheel with blades. The flow is cut and divided into two parts - up and down. A wheel with a small number of blades rotates these flows. The wheel itself rotates the auger from the motor.The motor is powered by electricity. Pressure builds up inside the pump and the liquid/gas is forced out into the side outlet pipe.
In vortex pumps, water is supplied not to the wheel, but along the rotation of the blades, and here there are more blades than in a centrifugal pump. The motor still rotates the auger, on which a wheel with blades is mounted. Water moves in the direction of the blades and is pushed out into the exit pipe. The latter is usually located parallel to the incoming one.
Vortex and centrifugal pumps differ in the method of water supply and the number of blades. Because of this, other differences emerge - vortex ones have low efficiency (45%), centrifugal ones are sensitive to air and solid particles - they can break / jam.

The content of the article
Advantages and disadvantages
Centrifugal pumps:
- High-performance, powerful and efficient (they pump water quickly, the productivity of household models reaches 1200 liters per hour, industrial models - up to 4000 liters per hour).
- High pressure of outgoing water.
- They last a long time and rarely break.
But:
- Designed only for heavy loads (if there is not enough water, it will not be able to exit through the pipe).
- Sensitive to air (if air gets inside, the device will stop).
- They require stable power supply (voltage surges will quickly damage the device).
- Expensive.
Vortex:
- Cheaper.
- Easier to repair.
- It's still air.
- Designed for medium loads/low productivity.
- Maximum head – 240 m.
- Low power (maximum 25 kilowatts).
- Low efficiency (45%).
Which is better: a vortex pump or a centrifugal pump?
Based on their characteristics, centrifugal pumps are better. But it all depends on the situation:
For domestic use we recommend a vortex pump. Its productivity will be 400-1000 liters per hour, it is not afraid of air bubbles, and they can be installed at depths below 9 meters.
If you need a more powerful device - up to 1500 liters per hour, use a centrifugal pump. But it should be installed no deeper than 9 meters, and there should be an intense load.
Table of criteria for choosing a pump
| Centrifugal models | Vortex models | |
| Silent | Yes | No |
| Dimensions | Large | Medium and small |
| Maximum depth for efficient work | Up to 9 meters | Up to 20 meters |
| Can it be installed at home? | Yes | Yes, but it will make a lot of noise (not recommended) |
| Efficiency | 97% | Up to 45% |
| Sensitivity to air bubbles | Yes | No |
| Maximum performance | 1500 liters per minute (domestic) 4000 l/m (production) | 1000 liters per minute |





