Drainage system in a private house: how to calculate storm drainage
Creating a reliable drainage system in a private home is a critical aspect of construction and landscaping. It protects the building and surrounding area from damage caused by rain and melt water. In this article we will look in detail at how to calculate rainwater drainage and storm drainage. We will also give advice to ensure their effectiveness and reliability.
The content of the article
The value of accurate calculation
Designing rainwater and storm drainage systems is critical to preventing potential flooding, soil erosion, and landscape damage. An improperly designed system will not only increase risks to your property. It will lead to the need for expensive repairs and system upgrades.
Design begins with calculating the rainwater that the system will need to process. This calculation takes into account the following factors:
- average annual precipitation for your area;
- water collection area;
- the ability of soil to absorb moisture.
These factors help determine the amount of water that needs to be drained to avoid potential problems.
How to calculate: steps and examples
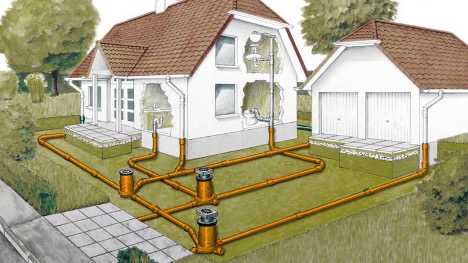
In order to accurately design a drainage system, it is necessary to carry out a hydraulic calculation of rainwater drainage and storm drainage. These calculations help determine the optimal pipe sizes and slopes. They also determine the location of drainage elements.
The basis for the calculation is a formula that takes into account the following data:
- Precipitation intensity.
- Runoff coefficient (depending on surface type).
- Water collection area.
- Safety factors.
An example of a hydraulic calculation of a storm sewer may look like this:
- determining the maximum flow of water that can occur during the heaviest rainfall;
- choosing a pipe diameter capable of providing discharge without overflow.
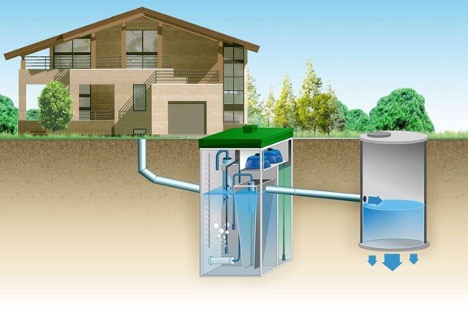
Before moving on to the details of the calculation, it is important to understand the main components of the system:
- pipes and sewer trays for transporting water;
- receiving wells and storm drains for collecting water;
- drainage fields or wells to filter and absorb water into the soil.
Principles of calculation and design
Calculating the diameter of a storm drain is a key design stage. It is based on the maximum possible volume of water that the system must pass. It is important to take into account all possible risk factors. Also, do not forget about the variability of weather conditions. The calculation involves analyzing data on local precipitation and the types of surfaces that collect water. It also takes into account the ability to absorb precipitation.
To determine the required pipe diameter, a formula is used that takes into account the water flow speed and the cross-sectional area of the pipe. This ensures that even in heavy rain conditions the system can effectively drain water.After all, it is important to prevent its stagnation and possible damage to structures and landscapes.
It is also important to consider integrating the drainage system with existing natural landscapes and waterways, which can help reduce stress on the system and improve its sustainability.
An example of the correct calculation of the diameter of a storm drain

This example demonstrates the basic steps for calculating the diameter of a storm drain. However, it is important to understand that each project is unique, and additional data and adjustments may be required for an accurate calculation, including taking into account the slope of the pipes, local climatic conditions and landscape features. It is recommended to involve qualified specialists in the calculations who can take into account all the necessary parameters and standards.
What will result from an incorrect calculation:
- Pipe diameters that are too small will not provide adequate drainage during heavy rainfall, causing the system to overflow.
- Insufficient sewerage capacity can cause flooding of the site, basements and first floors of houses, which causes damage to property.
- Excessive water accumulation can lead to erosion and soil erosion on the site, which threatens landscaping and building foundations.
- The accumulation of water can cause the destruction of walkways, driveways and other landscaping features.
- High humidity and standing water create favorable conditions for the development of mold and mildew, which negatively affects the health of residents.
- An incorrectly designed system requires frequent repairs, upgrades and maintenance, which leads to unjustified financial costs.
- Violation of wastewater codes and standards can result in administrative liability and lawsuits from neighbors or government agencies.
- Improper stormwater drainage can allow pollutants to enter local waterways, which can negatively impact the environment.
Correct calculation and design of the drainage system is the key to long-term safety and comfort of life in a private home. Errors in calculations can lead to serious and costly consequences.
Conclusion
Careful calculation of storm drainage and rainwater drainage not only protects your home and site from the negative effects of water, but also helps maintain the ecological balance in your region. Hiring qualified specialists to design and install a drainage system will allow you to avoid many problems in the future and guarantee the safety and comfort of your home.



