One-pipe and two-pipe heating systems: which is better, differences
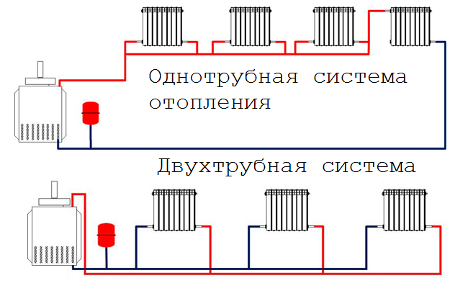
There is a single-pipe and two-pipe heating system. The first scheme involves supplying and discharging liquid through the same riser, and the second through different ones. Each type has its own characteristics, so it is impossible to say unequivocally that one is better and the other worse. A visual description of the design of each system, its advantages and disadvantages can be found in this article.
The content of the article
Design and types of one-pipe system
To understand which heating system is better - one-pipe or two-pipe, it is necessary to consider the design of each circuit, its pros and cons. Judging by the name, a one-pipe and two-pipe system are fundamentally different in the number of pipes:
- in the first case, water is supplied and discharged through the same channel;
- in the second, the supply goes through one riser, and the discharge through another.
Moreover, the main elements of the contour are the same. This is the riser itself, radiators, as well as pumps, taps and valves that regulate the flow of coolant and help bleed air.
One- and two-pipe heating systems work approximately the same. The water is heated by the boiler, enters the common house riser, and then sequentially flows into each radiator. Then, through the same pipe (return) it again goes to the boiler, where it is heated again, and the cycle is repeated many times.To ensure constant movement and approximately the same speed, one or more circulation pumps are connected to the system.
Moreover, the difference between a two-pipe heating system and a single-pipe one is due precisely to the fact that if there are 2 risers, the liquid is supplied through one of them and discharged through the other.
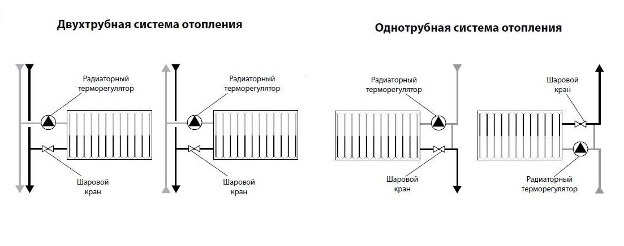
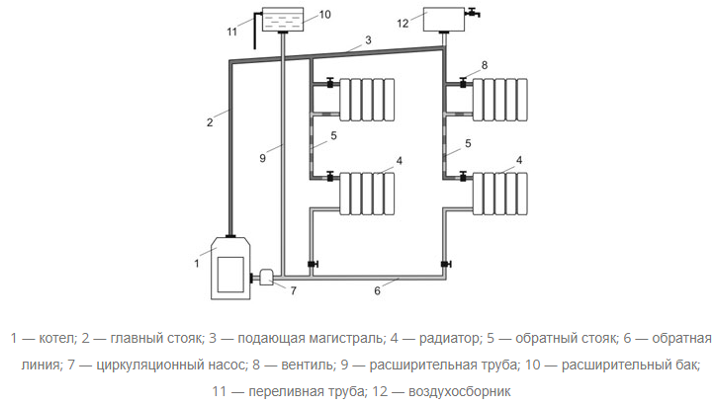
The water supply line may be located above or below the house. Depending on this, there are 2 types:
- with top wiring;
- with bottom wiring.
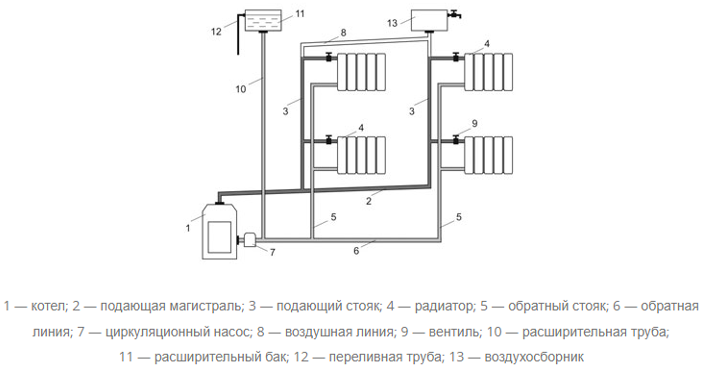
In the first case, hot water first goes to the attic and then flows sequentially to each radiator. In the second, it goes from the bottom up, filling the radiators, and then returns along the return line to the boiler. These diagrams show what a single-pipe and two-pipe heating system is, and what their fundamental difference is.
Pros and cons of a single-pipe system
A system with one riser was often installed in houses of the so-called Leningrad series with more spacious kitchens and wide entrances. Today it is used to a limited extent in low-rise and private houses.
Advantages such a device are obvious:
- Fewer materials are used, resulting in lower costs;
- since only one riser is installed, installation is simplified;
- the appearance is more attractive - there are fewer communications, and they can be hidden, for example, under a decorative box;
- simple control of water movement - you can turn off just one radiator and the current will stop;
- if necessary, you can connect only a few batteries in series, and not all at the same time.
But flaws A single-pipe heating system is also essential:
- after a long stoppage of operation, starting the circuit will take a long time;
- heat loss is greater, therefore heating costs increase;
- radiators warm up at different speeds - first the first ones, installed closer to the boiler, then the subsequent ones and lastly the outer ones;
- If there is a need for repairs, you will have to turn off all the radiators at once, which can lead to severe cooling of the house, especially in winter.
Design and types of two-pipe system
As already mentioned, the difference between a single-pipe and a two-pipe heating system is related to the number of pipes. In the first case, water moves through one riser. In the second, it enters through the supply and is discharged into a completely different circuit.
Such a circuit began to be installed in the 1930s. into Stalin-type houses (“Stalinka”). Then its use was temporarily abandoned due to the more affordable price of the single-pipe system. But now they are returning again to the 2-circuit circuit, since it is more efficient.
The two-pipe system also has several varieties. For example, it can have horizontal and vertical wiring.
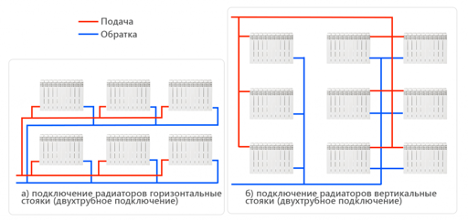
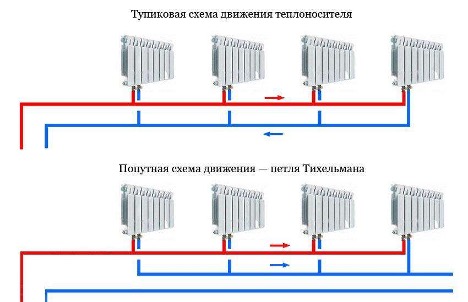
Depending on the trajectory of fluid movement, 2 more types are distinguished:
- With dead-end current.
- With a passing current (another name is the Tichelman loop).
In the first case, the coolant is sequentially supplied to each battery up to the last (conditionally dead-end) and is also removed from each radiator through the return line. In this case, the directions of movement are opposite, as shown in the diagram.
In the case of the Tichelman loop, the directions are the same due to the installation of an additional section of the circuit. The return collects liquid from each radiator, and then leaves the room and carries the water into the general circuit.This is a more complex system, but it provides the same pressure and speed of water, which practically eliminates emergency situations.
Pros and cons of a two-pipe system
It’s quite easy to understand which is better – heating using a single-pipe or two-pipe system if you study the advantages of the latter:
- all batteries warm up evenly, regardless of where exactly they are installed;
- you can adjust the temperature in any specific radiator if you install a thermostat;
- even if 1-2 batteries break, you can simply turn off the taps and replace them without turning off the heating throughout the house;
- a two-pipe circuit is a more universal solution, as it is suitable even for very tall apartment buildings and office buildings.
It is clear that a system with two risers does not have the disadvantages of a single-pipe heating system. But it has its drawbacks, which should not be written off either:
- costs increase significantly due to the need to install 2 water pipelines;
- installation becomes more complicated and will take longer;
- Since there are more communications, it is more difficult to hide them, for example, in a wall or in the floor.
Which circuit to put
It remains to figure out which heating system to choose - one-pipe or two-pipe. This question can only be answered taking into account the characteristics of the building. If it is a high-rise apartment building, most often a circuit with 2 risers is installed in it, because it ensures efficient heating of all radiators. In addition, in the event of an accident or the need for repairs, it is enough to dismantle only a few radiators without turning off the heating of the entire system.
If we are talking about a private, low-rise building (within 5 floors), a single-pipe scheme can be implemented. It will cost less and is easier to install.In addition, there are not so many communications, and it is easier to hide them, for example, in the floor. As for the shortcomings, in the case of a small house they are practically not felt. If the boiler is working properly, the entire circuit warms up in a matter of hours.
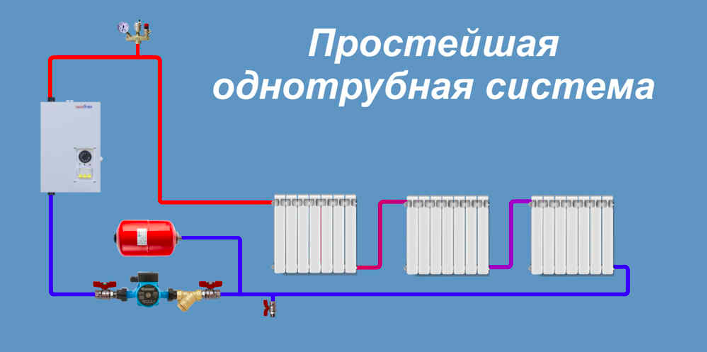
From this review it is clear which heating is better - single-pipe or two-pipe. It is impossible to give a definite answer here, since everything depends on the area and number of floors of the building. If the circuit is long, it is better to implement a scheme with 2 risers. For private and low-rise houses, a single-pipe system is also quite suitable.





