Radiant heating system for a private apartment building: what it looks like, diagram
The radiant heating system is a modern method of heating rooms, which is increasingly being used both in private homes and in multi-apartment residential complexes. Its essence lies in the uniform distribution of heat throughout the entire volume of the room thanks to a special wiring diagram. This method is highly efficient and economical compared to traditional heating systems.

The content of the article
Radiant heating system for a private house: features and advantages
A radiant heating system for a private home opens up new opportunities for creating a comfortable and economical microclimate in the living space. Based on the principle of uniform heat distribution throughout all rooms, this system avoids overheating or overcooling of individual zones. Unlike traditional heating systems, radiant heating provides more precise temperature control, which helps create an optimal level of comfort in your home.
The advantages of a radiant heating system for a private home are numerous and deserve special attention:
- The efficiency of this type of heating is significantly higher than that of alternative systems. Heat losses are minimized by optimizing the coolant distribution scheme.
- The system allows you to individually regulate the temperature in each room.This not only increases the level of comfort for residents, but also helps save energy resources.
- Radiant heating distribution is highly reliable and durable, due to the absence of the need for frequent maintenance and repair of the system.
Another important advantage is the environmental friendliness of the radiant heating system. Due to more efficient use of coolant and the possibility of using low-temperature heat sources such as heat pumps or solar collectors, the environmental impact is reduced. This makes a radiant heating system not only profitable, but also a responsible choice for the modern homeowner seeking to create a cozy and environmentally friendly home.
Operating principle and diagram of a radiant heating system
This principle is based on the uniform distribution of thermal energy throughout the entire volume of the room using a special pipe layout running under the floor or inside the walls. Unlike traditional radiator systems, where heat is transferred primarily through convection, radiant heating uses predominantly radiant heat, providing a more natural and comfortable warmth.
The radiant heating system diagram includes the following key elements:
- A heat generator (boiler or heat pump) that produces thermal energy.
- A collector (distribution unit) that distributes the coolant through the pipes of the system.
- Pipes for heated floors or built into walls/ceilings through which coolant (water or antifreeze) circulates, evenly distributing heat throughout the room.
- Control automation, including thermostats in each room to regulate the temperature according to individual preferences.
The fundamental difference between radial heating distribution is that each pipe circuit is laid from the collector directly to the heating zone and back. This allows for maximum efficiency and savings by minimizing heat loss during the transfer process and allowing precise temperature adjustments in different parts of the house.
The collector-beam design allows not only to efficiently distribute heat, but also to easily integrate various heat sources into the system, such as solar collectors or geothermal pumps, making it an ideal solution for creating multi-energy heating systems.
An important feature of radiant heating is also the possibility of using it not only for heating, but also for cooling rooms in the summer, which is achieved by passing cooled coolant through the system. This makes the radiant heating system a universal and highly effective solution for creating a comfortable climate in the home all year round.
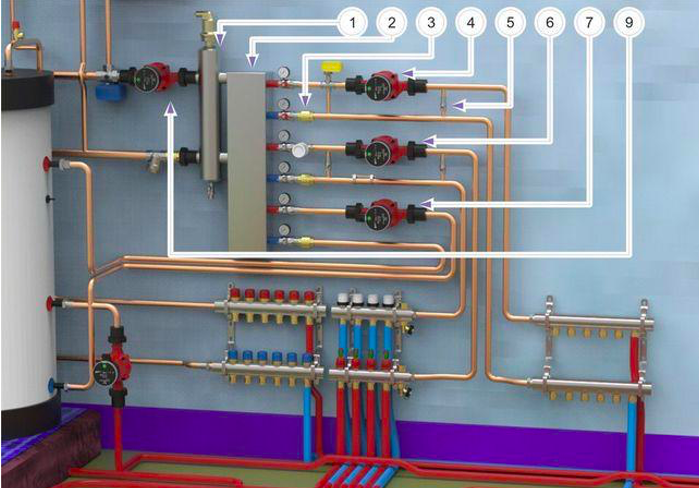
Radiant heating: application in apartment buildings
The use of a radiant heating system in an apartment building becomes possible thanks to the use of individual heating points and collectors on each floor or in each apartment. This provides a high level of comfort for all residents and allows each user to independently regulate the heat supply of their home.
Advantages and disadvantages
Before implementing a radiant heating system, it is worth taking a balanced approach to analyzing its pros and cons:
- Pros include high efficiency, energy savings, the ability to individually control heating in each room, and reduced risk of leaks and accidents by minimizing pipe connections.
- Disadvantages may include the relative complexity of installation and the higher initial costs of installing the system compared to traditional heating methods.
Conclusion
When choosing a radiant heating system for a two-story house or any other property, it is important to consider not only the economic benefits, but also the level of comfort that it can provide. Radiant heating systems offer an innovative approach to space heating that can be an ideal solution for many homeowners seeking to create the most comfortable and energy-efficient living conditions.




