Indoor air infiltration coefficient: table, calculation
The air infiltration coefficient plays a key role in creating a healthy and comfortable indoor climate. This parameter affects the energy efficiency of buildings, indoor air quality and the overall comfort of living or working.
The content of the article
What is air infiltration?
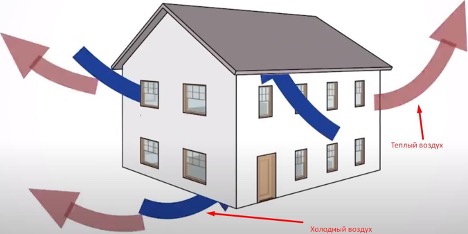
Air infiltration is the process of penetration of outside air into a room through various leaks, cracks and other imperfections in the building envelope. This process can be either natural or artificially created. Natural infiltration occurs due to the difference in pressure inside and outside the building, as well as due to the wind load on the building.
Air infiltration plays a key role in indoor air quality and ventilation. On the one hand, it helps maintain the required level of fresh air, ensuring the removal of pollutants, excess humidity and carbon dioxide. On the other hand, excessive infiltration can lead to heat loss, increased heating and cooling costs, and the creation of drafts and reduced living or working comfort.
Controlling air infiltration is an important part of building design and operation, especially given today's energy efficiency requirements.To minimize unwanted infiltration, various methods are used to improve the airtightness of buildings, including installing quality windows and doors, improving seals and insulating materials. Special ventilation systems are also used that provide the necessary air exchange without significant heat loss.
How is infiltration coefficient measured?
The infiltration coefficient of a building is measured as the volume of air entering a room per unit time at a given pressure. This coefficient is usually expressed in m³/m² h at a pressure difference of 10 Pa. It is important to understand that infiltration rates depend on many factors, including the quality of building construction, the presence and quality of seals, and climatic conditions.
Design infiltration coefficient
The design infiltration coefficient is an important parameter in assessing the energy efficiency of buildings. It shows how much air enters the room through various leaks in the structure over a certain period of time.
Calculation of the infiltration coefficient is usually carried out using special equipment and techniques. One common method is the blower door test. It measures the amount of air required to maintain a certain pressure (often 50 Pa) in a building. The calculation is made using the formula:

The infiltration coefficient depends on many factors:
- The quality and age of building materials, as well as the qualifications of workers, affect the tightness of the building.
- Windows and doors that do not close tightly will significantly increase infiltration.
- Strong winds and temperature differences between indoors and outdoors can increase infiltration.
- The availability and efficiency of ventilation systems also play an important role.
Understanding and controlling the infiltration coefficient allows you to:
- reducing unwanted infiltration reduces energy consumption for heating and cooling;
- eliminating drafts and maintaining optimal air exchange help create a comfortable environment;
- controlled infiltration ensures the necessary air exchange, preventing problems with humidity and air pollution.
Practical application and standards
The table shows standard values of infiltration coefficients for various types of buildings:
- residential buildings: from 0.5 to 3.0 m³/m²·h;
- office buildings: from 2.0 to 4.0 m³/m²·h;
- industrial buildings: from 3.0 to 6.0 m³/m²·h.
Approximate table of air infiltration coefficients:
| Building type | Infiltration coefficient (m³/m² h) |
|---|---|
| Residential buildings (old construction) | 3.0 — 5.0 |
| Residential buildings (modern construction) | 1.0 — 3.0 |
| Office buildings | 2.0 — 4.0 |
| Industrial building | 3.0 — 6.0 |
| Buildings with increased requirements for airtightness (for example, laboratories) | 0.5 — 1.5 |
The Importance of Air Infiltration in Energy Efficiency
Air infiltration is a key factor affecting the energy efficiency of buildings. Too high an infiltration rate can lead to increased heat loss and increased heating costs. On the other hand, insufficient infiltration can lead to poor indoor air quality and, as a result, reduced occupant comfort and health.
Conclusion
The air infiltration coefficient is an important indicator that must be taken into account when designing, constructing and operating buildings.Correct calculation and control of this parameter helps to achieve an optimal balance between energy efficiency and living comfort.