Induction crucible furnace: what is it, principle of operation, diagram
A crucible furnace is a high-temperature industrial equipment designed for melting metals, alloys and other materials in a specialized container called a crucible. A distinctive feature of such a furnace is the ability to precisely control the temperature and time of the process, which ensures high purity and uniformity of the resulting product.

The content of the article
Where are crucible furnaces most often used?
Crucible furnaces are widely used in the metallurgical industry, where they are used for melting and remelting various types of metals and alloys. In this area, they are integral to the creation of materials with special characteristics, such as high strength, corrosion resistance and specific electromagnetic properties.
Other uses:
- in the chemical industry for the synthesis of high-purity substances;
- in jewelry for melting precious metals;
- in the glass industry for the production of high-quality glass;
- in medical production to create biocompatible materials;
- in research laboratories to experiment with various materials.
In the electronics industry, crucible furnaces play a key role in the creation of semiconductor materials and microelectronic components.They provide the precision and repeatability needed to meet the stringent standards of quality and efficiency in this high-tech industry.
How a stove works in simple words
An induction crucible furnace works by creating a magnetic field that heats the crucible and the contents inside it. This heating method is more efficient and economical than traditional methods. The operating principle of an induction crucible furnace is based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.
Important components:
- An induction coil, it creates a magnetic field.
- The crucible stores the molten material.
Advantages:
- high efficiency;
- minimizing energy losses;
- Possibility of precise temperature control.
Key parameters
Calculation is a critical stage in the process of its design and operation. The efficiency and reliability of the furnace largely depend on the accuracy and adequacy of these calculations. Let's look at the key parameters that need to be taken into account.
One of the most important parameters is the power of the induction coil, which affects the melting rate of the material and the energy efficiency of the system. The frequency of the induction field is also significant, since the depth of penetration of the magnetic field and, accordingly, the quality of heating depend on it.
It is important to calculate thermal characteristics such as heat transfer coefficient and heat loss through the crucible walls. This is necessary to determine the optimal cooling parameters and insulation levels.
The dimensions, shape of the crucible and induction coil have a direct impact on the efficiency of the system. Geometric parameters must be optimized to maximize heating quality and minimize electromagnetic losses.
Additionally, the electromagnetic compatibility of the system should be considered to avoid unwanted electromagnetic interference in the environment or to other devices.
In general, the calculation of an induction crucible furnace requires an integrated and multi-parameter approach. Effective design is only possible with careful consideration of all the above factors. This, in turn, will provide the foundation for high-performance and reliable operation of the furnace.
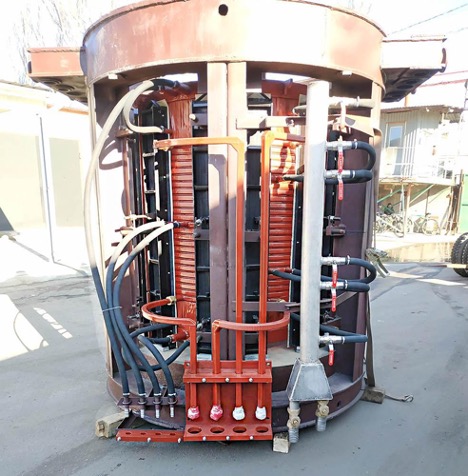
Diagram of an induction crucible furnace
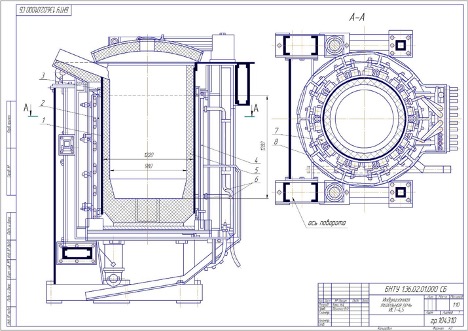
The scheme usually includes the following key components:
- Electronic control unit. This unit is responsible for regulating the power and frequency of the induction coil. It can be equipped with a display and interfaces for monitoring and controlling oven parameters.
- Induction coil. This is a ring of conductor that creates a magnetic field when electric current is passed through it. The coil surrounds the crucible and is the main source of heat.
- Crucible. This component, usually made from materials that can withstand high temperatures (such as graphite or ceramic), contains a meltable material.
- Cooling system. To maintain optimal operating conditions and prevent components from overheating.
- Temperature and pressure sensors. They monitor conditions inside the furnace and send data to the electronic control unit for possible correction of parameters.
These elements of the induction crucible furnace circuit interact to provide an efficient and safe process for melting materials. All parameters are typically managed automatically, minimizing the possibility of errors and increasing overall system performance.
Features and Application
The cold crucible has a number of unique features that make it preferable in certain scenarios. In particular, it is not directly heated, reducing the risk of oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions during the smelting process. This is especially important when working with reactive or oxidation-sensitive materials.
A crucible furnace for aluminum is the optimal choice in the metallurgy of this metal. Aluminum requires very precise temperature control to avoid the creation of defects and unwanted phases in the resulting alloys. At the same time, the use of a cold crucible further minimizes the risks of oxidation and ensures a high degree of purity of the material.
These characteristics make cold crucible and crucible furnaces for aluminum ideal tools for use in high-tech industries such as aerospace, electronics, and the production of high-quality components for various engineering systems.
Conclusion
Induction crucible furnaces are a high-tech solution for melting and processing of metals and other materials. In terms of financial efficiency and operational reliability, these ovens provide significant advantages. They are especially relevant in industrial sectors where high standards of quality and process efficiency are required.





